9.3: Spinal Reflexes
- Page ID
- 137400
This page is a draft and under active development. Please forward any questions, comments, and/or feedback to the ASCCC OERI (oeri@asccc.org).
- Distinguish between the types of spinal reflexes
Spinal reflexes include the stretch reflex, the Golgi tendon reflex, the crossed extensor reflex, and the withdrawal reflex.
Stretch Reflex
The stretch reflex (myotatic reflex) is a muscle contraction in response to stretching within the muscle. This reflex has the shortest latency of all spinal reflexes. It is a monosynaptic reflex that provides automatic regulation of skeletal muscle length.
When a muscle lengthens, the muscle spindle is stretched and its nerve activity increases. This increases alpha motor neuron activity, causing the muscle fibers to contract and thus resist the stretching. A secondary set of neurons also causes the opposing muscle to relax. The reflex functions to maintain the muscle at a constant length.
Golgi Tendon Reflex
The Golgi tendon reflex is a normal component of the reflex arc of the peripheral nervous system. The tendon reflex operates as a feedback mechanism to control muscle tension by causing muscle relaxation before muscle force becomes so great that tendons might be torn.
Although the tendon reflex is less sensitive than the stretch reflex, it can override the stretch reflex when tension is great, making you drop a very heavy weight, for example. Like the stretch reflex, the tendon reflex is ipsilateral.
The sensory receptors for this reflex are called Golgi tendon receptors, and lie within a tendon near its junction with a muscle. In contrast to muscle spindles, which are sensitive to changes in muscle length, tendon organs detect and respond to changes in muscle tension that are caused by a passive stretch or muscular contraction.
Crossed Extensor Reflex
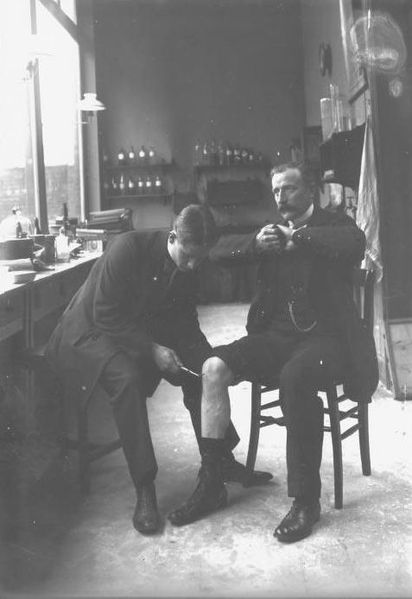

Jendrassik maneuver: The Jendrassik maneuver is a medical maneuver wherein the patient flexes both sets of fingers into a hook-like form and interlocks those sets of fingers together (note the hands of the patient in the chair). This maneuver is used often when testing the patellar reflex, as it forces the patient to concentrate on the interlocking of the fingers and prevents conscious inhibition or influence of the reflex.
The crossed extensor reflex is a withdrawal reflex. The reflex occurs when the flexors in the withdrawing limb contract and the extensors relax, while in the other limb, the opposite occurs. An example of this is when a person steps on a nail, the leg that is stepping on the nail pulls away, while the other leg takes the weight of the whole body.
The crossed extensor reflex is contralateral, meaning the reflex occurs on the opposite side of the body from the stimulus. To produce this reflex, branches of the afferent nerve fibers cross from the stimulated side of the body to the contralateral side of the spinal cord. There, they synapse with interneurons, which in turn, excite or inhibit alpha motor neurons to the muscles of the contralateral limb.
Withdrawal Reflex
The withdrawal reflex (nociceptive or flexor withdrawal reflex) is a spinal reflex intended to protect the body from damaging stimuli. It is polysynaptic, and causes the stimulation of sensory, association, and motor neurons.
When a person touches a hot object and withdraws his hand from it without thinking about it, the heat stimulates temperature and danger receptors in the skin, triggering a sensory impulse that travels to the central nervous system. The sensory neuron then synapses with interneurons that connect to motor neurons. Some of these send motor impulses to the flexors to allow withdrawal.
Some motor neurons send inhibitory impulses to the extensors so flexion is not inhibited—this is referred to as reciprocal innervation. Although this is a reflex, there are two interesting aspects to it:
- The body can be trained to override that reflex.
- An unconscious body (or even drunk or drugged bodies) will not exhibit the reflex.
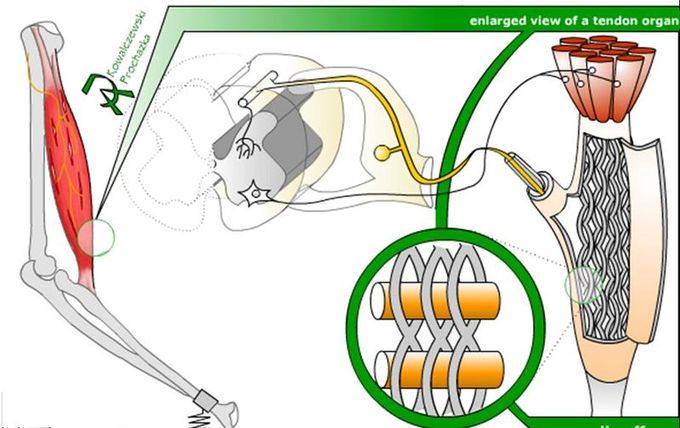
Golgi tendon organ: The Golgi tendon organ, responsible for the Golgi tendon reflex, is diagrammed with its typical position in a muscle (left), neuronal connections in spinal cord (middle), and expanded schematic (right). The tendon organ is a stretch receptor that signals the amount of force on the muscle and protects the muscle from excessively heavy loads by causing the muscle to relax and drop the load.
Key Points
- The stretch reflex is a monosynaptic reflex that regulates muscle length through neuronal stimulation at the muscle spindle. The alpha motor neurons resist stretching by causing contraction, and the gamma motor neurons control the sensitivity of the reflex.
- The stretch and Golgi tendon reflexes work in tandem to control muscle length and tension. Both are examples of ipsilateral reflexes, meaning the reflex occurs on the same side of the body as the stimulus.
- The crossed extensor reflex is a contralateral reflex that allows the body to compensate on one side for a stimulus on the other. For example, when one foot steps on a nail, the crossed extensor reflex shifts the body’s weight onto the other foot, protecting and withdrawing the foot on the nail.
- The withdrawal reflex and the more-specific pain withdrawal reflex involve withdrawal in response to a stimulus (or pain). When pain receptors, called nociceptors, are stimulated, reciprocal innervations stimulate the flexors to withdraw and inhibit the extensors to ensure they are unable to prevent flexion and withdrawal.
Key Terms
- golgi tendon reflex: A normal component of the reflex arc of the peripheral nervous system. In this reflex, a skeletal muscle contraction causes the agonist muscle to simultaneously lengthen and relax. This reflex is also called the inverse myotatic reflex because it is the inverse of the stretch reflex. Although muscle tension is increasing during the contraction, the alpha motor neurons in the spinal cord that supply the muscle are inhibited. However, antagonistic muscles are activated.
- alpha motor neuron: These are large, lower motor neurons of the brainstem and spinal cord. They innervate the extrafusal muscle fibers of skeletal muscle and are directly responsible for initiating their contraction. Alpha motor neurons are distinct from gamma motor neurons that innervate the intrafusal muscle fibers of muscle spindles.
ATTRIBUTIONS
CC LICENSED CONTENT, SHARED PREVIOUSLY
- Adapted from Anatomy and Physiology - Section 12.10C. Authored and Provided by: Boundless.com. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike


