12.6: Prejudice, Discrimination, and Stereotyping
- Page ID
- 10674
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \) \( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)\(\newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\) \( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\) \( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \(\newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\) \( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\) \( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)\(\newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
Introduction

Old-fashioned Biases: Almost Gone
Social Dominance Orientation

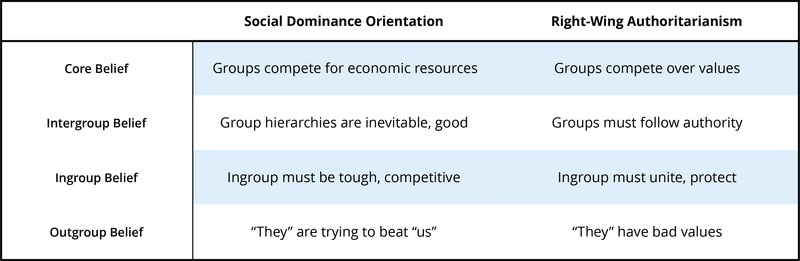
Right-wing Authoritarianism
20th Century Biases: Subtle but Significant
Automatic Biases

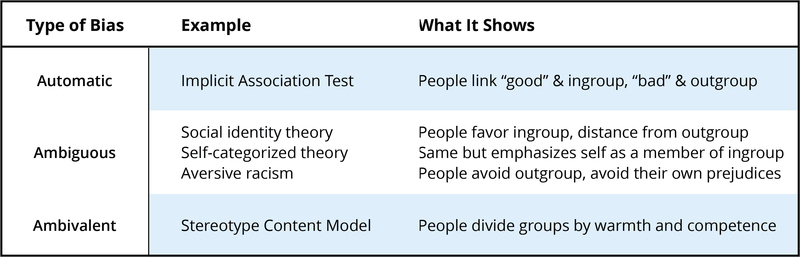
Ambiguous Biases

Bias Can Be Complicated - Ambivalent Biases
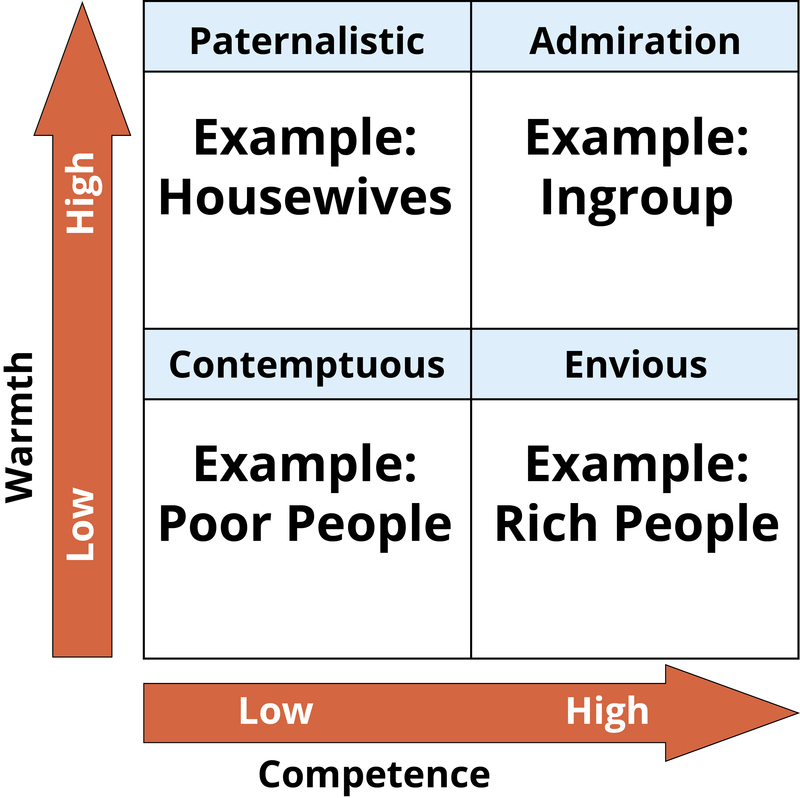
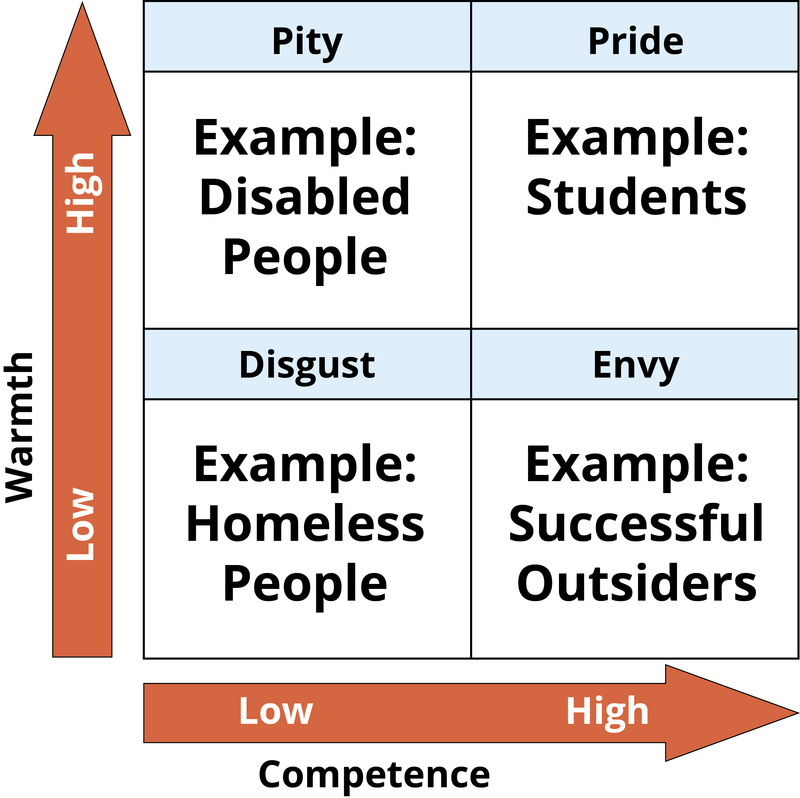
Conclusion: 21st Century Prejudices
Outside Resources
- Web: Website exploring the causes and consequences of prejudice.
- http://www.understandingprejudice.org/
Discussion Questions
Vocabulary
- Automatic bias
- Automatic biases are unintended, immediate, and irresistible.
- Aversive racism
- Aversive racism is unexamined racial bias that the person does not intend and would reject, but that avoids inter-racial contact.
- Blatant biases
- Blatant biases are conscious beliefs, feelings, and behavior that people are perfectly willing to admit, are mostly hostile, and openly favor their own group.
- Discrimination
- Discrimination is behavior that advantages or disadvantages people merely based on their group membership.
- Implicit Association Test
- Implicit Association Test (IAT) measures relatively automatic biases that favor own group relative to other groups.
- Prejudice
- Prejudice is an evaluation or emotion toward people merely based on their group membership.
- Right-wing authoritarianism
- Right-wing authoritarianism (RWA) focuses on value conflicts but endorses respect for obedience and authority in the service of group conformity.
- Self-categorization theory
- Self-categorization theory develops social identity theory’s point that people categorize themselves, along with each other into groups, favoring their own group.
- Social dominance orientation
- Social dominance orientation (SDO) describes a belief that group hierarchies are inevitable in all societies and even good, to maintain order and stability.
- Social identity theory
- Social identity theory notes that people categorize each other into groups, favoring their own group.
- Stereotype Content Model
- Stereotype Content Model shows that social groups are viewed according to their perceived warmth and competence.
- Stereotypes
- Stereotype is a belief that characterizes people based merely on their group membership.
- Subtle biases
- Subtle biases are automatic, ambiguous, and ambivalent, but real in their consequences.


