12.1.1: Physical Development in Middle Adulthood
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID
- 63332
Each person experiences age-related physical changes based on many factors: biological factors, such as molecular and cellular changes, and oxidative damage are called primary aging, while aging that occurs due to controllable factors, such as an unhealthy lifestyle including lack of physical exercise and poor diet, is called secondary aging (Busse, 1969). These factors are shown in Figure 8.1
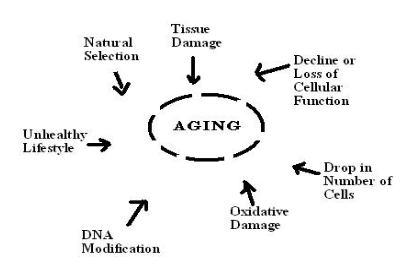
Getting out of shape is not an inevitable part of aging; it is probably due to the fact that middle adults become less physically active and have experienced greater stress. Smoking tobacco, drinking alcohol, poor diet, stress, physical inactivity, and chronic disease such as diabetes or arthritis reduce overall health. However, there are things can be done to combat many of these changes by adopting healthier lifestyles.
Physical Changes
Hair: When asked to imagine someone in middle adulthood, we often picture someone with the beginnings of wrinkles and gray or thinning hair. What accounts for these physical changes? Hair color is due to a pigment called melanin which is produced by hair follicles (Martin, 2014). With aging, the hair follicles produce less melanin and this causes the hair to become gray. Hair color typically starts turning lighter at the temples, but eventually all the hair will become white. For many, graying begins in the 30s, but it is largely determined by your genes. Gray hair occurs earlier in white people and later in Asians.

Genes also determine how much hair remains on your head. Almost everyone has some hair loss with aging, and the rate of hair growth slows with aging. Many hair follicles stop producing new hairs and hair strands become smaller. Men begin showing signs of balding by 30 and some are nearly bald by 60. Male-pattern baldness is related to testosterone and is identified by a receding hairline followed by hair loss at the top of the head. Figure 8.2 shows tennis champion Andre Agassi’s characteristic male- patterned baldness. Women can also develop female- patterned baldness as their hair becomes less dense and the scalp becomes visible (Martin, 2014). Sudden hair loss, however, can be a symptom of a health problem.
Skin: Skin continues to dry out and is prone to more wrinkling, particularly on the sensitive face area. Wrinkles, or creases in the skin, are a normal part of aging. As we get older, our skin dries and loses the underlying layer of fat, so our face no longer appears smooth. Loss of muscle tone and thinning skin can make the face appear flabby or drooping. Although wrinkles are a natural part of aging and genetics plays a role, frequent sun exposure and smoking will cause wrinkles to appear sooner. Dark spots and blotchy skin also occur as one ages and are due to exposure to sunlight (Moskowitz, 2014). Blood vessels become more apparent as the skin continues to dry and get thinner.
Sarcopenia: The loss of muscle mass and strength that occurs with aging is referred to as Sarcopenia (Morley, Baumgartner, Roubenoff, Mayer, & Nair, 2001). Sarcopenia is thought to be a significant factor in the frailty and functional impairment that occurs when older. The decline of growth and anabolic hormones, especially testosterone, and decreased physical activity have been implicated as causes of sarcopenia (Proctor, Balagopal, & Nair, 1998). This decline in muscle mass can occur as early as 40 years of age and contributes significantly to a decrease in life quality, increase in health care costs, and early death in older adults (Karakelides & Nair, 2005). Exercise is certainly important to increase strength, aerobic capacity, and muscle protein synthesis, but unfortunately it does not reverse all the age-related changes that occur. The muscle-to-fat ratio for both men and women also changes throughout middle adulthood, with an accumulation of fat in the stomach area.
Lungs: The lungs serve two functions: Supply oxygen and remove carbon dioxide. Thinning of the bones with age can change the shape of the rib cage and result in a loss of lung expansion. Age related changes in muscles, such as the weakening of the diaphragm, can also reduce lung capacity. Both of these changes will lower oxygen levels in the blood and increase the levels of carbon dioxide. Experiencing shortness of breath and feeling tired can result (NIH, 2014b). In middle adulthood, these changes and their effects are often minimal, especially in people who are non-smokers and physically active. However, in those with chronic bronchitis, or who have experienced frequent pneumonia, asthma other lung related disorders, or who are smokers, the effects of these normal age changes can be more pronounced.
Sensory Changes
Vision: A normal change of the eye due to age is presbyopia, which is Latin for “old vision.” It refers to a loss of elasticity in the lens of the eye that makes it harder for the eye to focus on objects that are closer to the person. When we look at something far away, the lens flattens out; when looking at nearby objects tiny muscle fibers around the lens enable the eye to bend the lens. With age these muscles weaken and can no longer accommodate the lens to focus the light. Anyone over the age of 35 is at risk for developing presbyopia. According to the National Eye Institute (NEI) (2016), signs that someone may have presbyopia include:
- Hard time reading small print
- Having to hold reading material farther than arm’s distance
- Problems seeing objects that are close
- Headaches
- Eyestrain
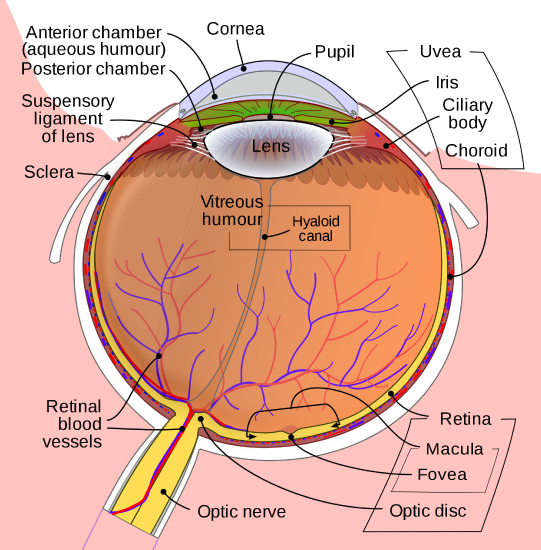
Another common eye problem people experience as they age are floaters, little spots or “cobwebs” that float around the field of vision. They are most noticeable if you are looking at the sky on a sunny day, or at a lighted blank screen. Floaters occur when the vitreous, a gel-like substance in the interior of the eye, slowly shrinks. As it shrinks, it becomes somewhat stringy, and these strands can cast tiny shadows on the retina. In most cases, floaters are harmless, more of an annoyance than a sign of eye problems. However, floaters that appear suddenly, or that darken and obscure vision can be a sign of more serious eye problems, such a retinal tearing, infection, or inflammation. People who are very nearsighted (myopic), have diabetes, or who have had cataract surgery are also more likely to have floaters (NEI, 2009).
During midlife, adults may begin to notice a drop in scotopic sensitivity, the ability to see in dimmer light. By age 60, the retina receives only one third as much light as it did at age 20, making working in dimmer light more difficult (Jackson & Owsley, 2000). Night vision is also affected as the pupil loses some of its ability to open and close to accommodate drastic changes in light. Eyes become more sensitive to glare from headlights and street lights making it difficult to see people and cars, and movements outside of our direct line of sight (NIH, 2016c).
Finally, some people experience dry eye syndrome, which occurs when the eye does not produce tears properly, or when the tears evaporate too quickly because they are not the correct consistency (NEI, 2013). While dry eye can affect people at any age, nearly 5 million Americans over the age of 50 experience dry eye. It affects women more than men, especially after menopause. Women who experienced an early menopause may be more likely to experience dry eye, which can cause surface damage to the eye.
Hearing: Hearing problems increase during middle adulthood. According to a recent UK study (Dawes et al., 2014), the rate of hearing problems in their sample doubled between the ages of 40 and 55 and tripled by age 64. Similar statistics are found in U.S. samples of middle-aged adults. Prior to age 40, about 5.5% of adults report hearing problems. This jumps to 19% among 40 to 69 year-olds (American Psychological Association, 2016). Middle-aged adults may experience more problems understanding speech when in noisy environments, in comparison to younger adults (Füllgrabe, Moore, & Stone, 2015; Neidleman, Wambacq, Besing, Spitzer, & Koehnke, 2015).
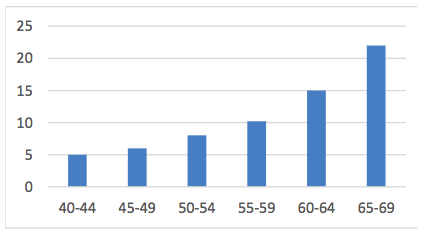
As we age we also lose the ability to hear higher frequencies (Humes, Kewley-Port, Fogerty, & Kinney, 2010). Hearing changes are more common among men than women, but males may underestimate their hearing problems (Uchida, Nakashima, Ando, Niino, & Shimokata, 2003). For many adults, hearing loss accumulates after years of being exposed to intense noise levels. Men are more likely to work in noisy occupations. Hearing loss is also exacerbated by cigarette smoking, high blood pressure, and stroke. Most hearing loss could be prevented by guarding against being exposed to extremely noisy environments.


