Self-Check Questions
Q1
Identify the most accurate statement. A price floor will have the largest effect if it is set:
- substantially above the equilibrium price
- slightly above the equilibrium price
- slightly below the equilibrium price
- substantially below the equilibrium price
Sketch all four of these possibilities on a demand and supply diagram to illustrate your answer.
Q2
A price ceiling will have the largest effect:
- substantially below the equilibrium price
- slightly below the equilibrium price
- substantially above the equilibrium price
- slightly above the equilibrium price
Sketch all four of these possibilities on a demand and supply diagram to illustrate your answer.
Q3
Select the correct answer. A price floor will usually shift:
- demand
- supply
- both
- neither
Illustrate your answer with a diagram.
Q4
Select the correct answer. A price ceiling will usually shift:
- demand
- supply
- both
- neither
Critical Thinking Questions
Q6
Why are the factors that shift the demand for a product different from the factors that shift the demand for labor? Why are the factors that shift the supply of a product different from those that shift the supply of labor?
Q7
During a discussion several years ago on building a pipeline to Alaska to carry natural gas, the U.S. Senate passed a bill stipulating that there should be a guaranteed minimum price for the natural gas that would be carried through the pipeline. The thinking behind the bill was that if private firms had a guaranteed price for their natural gas, they would be more willing to drill for gas and to pay to build the pipeline.
- Using the demand and supply framework, predict the effects of this price floor on the price, quantity demanded, and quantity supplied.
- With the enactment of this price floor for natural gas, what are some of the likely unintended consequences in the market?
- Suggest some policies other than the price floor that the government can pursue if it wishes to encourage drilling for natural gas and for a new pipeline in Alaska.
Solution
S1
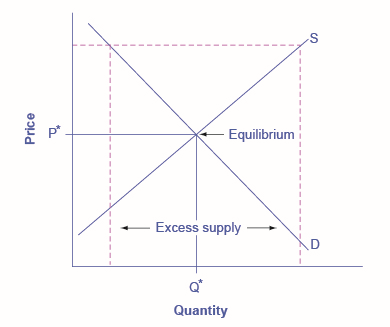
A price floor prevents a price from falling below a certain level, but has no effect on prices above that level. It will have its biggest effect in creating excess supply (as measured by the entire area inside the dotted lines on the graph, from \(D\) to \(S\)) if it is substantially above the equilibrium price. This is illustrated in the following figure.
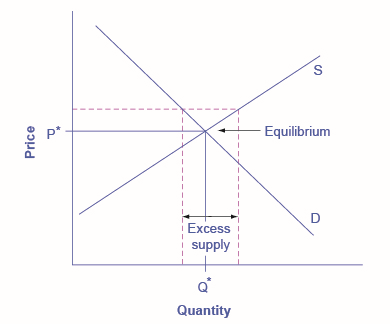
It will have a lesser effect if it is slightly above the equilibrium price. This is illustrated in the next figure.
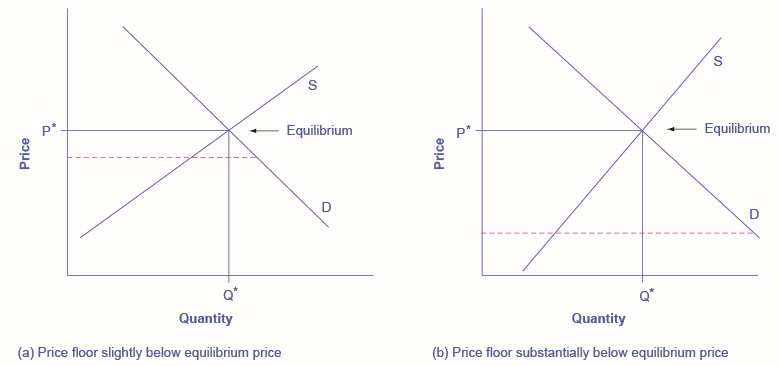
It will have no effect if it is set either slightly or substantially below the equilibrium price, since an equilibrium price above a price floor will not be affected by that price floor. The following figure illustrates these situations.
S2
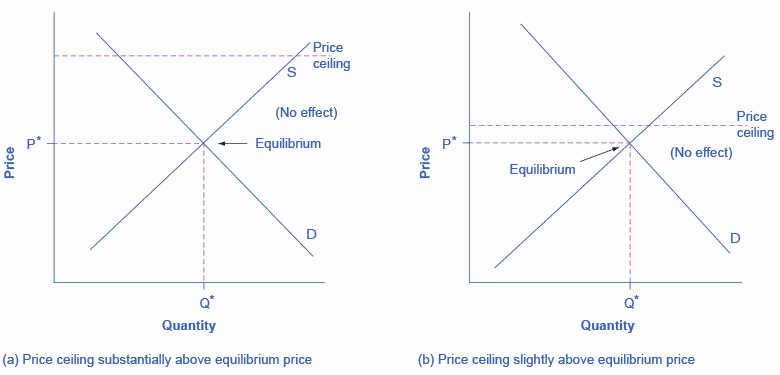
A price ceiling prevents a price from rising above a certain level, but has no effect on prices below that level. It will have its biggest effect in creating excess demand if it is substantially below the equilibrium price. The following figure illustrates these situations.
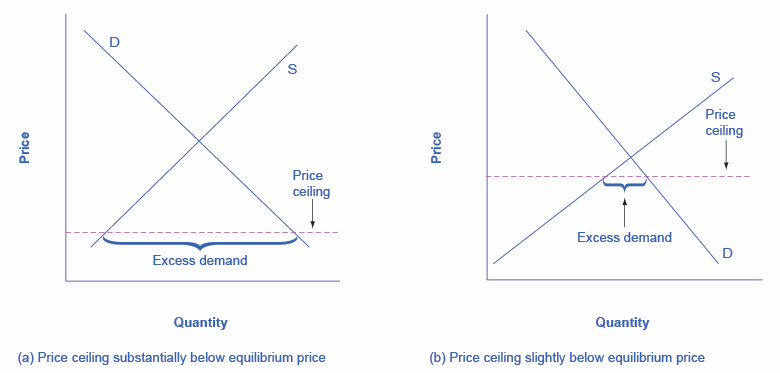
When the price ceiling is set substantially or slightly above the equilibrium price, it will have no effect on creating excess demand. The following figure illustrates these situations.
S3
Neither. A shift in demand or supply means that at every price, either a greater or a lower quantity is demanded or supplied. A price floor does not shift a demand curve or a supply curve. However, if the price floor is set above the equilibrium, it will cause the quantity supplied on the supply curve to be greater than the quantity demanded on the demand curve, leading to excess supply.
S4
Neither. A shift in demand or supply means that at every price, either a greater or a lower quantity is demanded or supplied. A price ceiling does not shift a demand curve or a supply curve. However, if the price ceiling is set below the equilibrium, it will cause the quantity demanded on the demand curve to be greater than the quantity supplied on the supply curve, leading to excess demand.







