8.07: Appendix G: Stages of Listening
- Page ID
- 134510
44
Appendix G: Stages of Listening
Rebekah Bennetch, Corey Owen, and Zachary Keesey
Stages of the Listening Process
Listening is a skill of critical significance in all aspects of our lives, from maintaining our personal relationships, to getting our jobs done, to taking notes in class, to figuring out which bus to take to the airport. Regardless of how we’re engaged with listening, it’s important to understand that listening involves more than just hearing the words that are directed at us. Listening is an active process by which we make sense of, assess, and respond to what we hear.
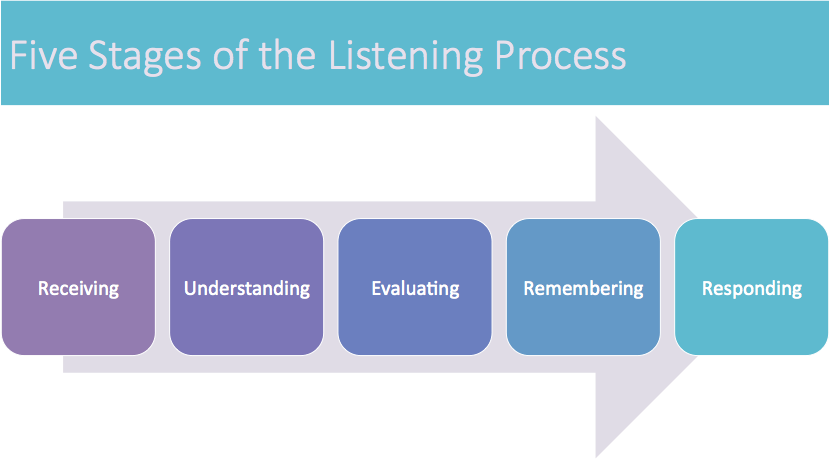
The listening process involves five stages: receiving, understanding, evaluating, remembering, and responding. These stages will be discussed in more detail in later sections. An effective listener must hear and identify the speech sounds directed toward them, understand the message of those sounds, critically evaluate or assess that message, remember what’s been said, and respond (either verbally or nonverbally) to information they’ve received.
Effectively engaging in all five stages of the listening process lets us best gather the information we need from the world around us.
Active Listening
Active listening is a particular communication technique that requires the listener to provide feedback on what he or she hears to the speaker, by way of restating or paraphrasing what they have heard in their own words. The goal of this repetition is to confirm what the listener has heard and to confirm the understanding of both parties. The ability to actively listen demonstrates sincerity, and that nothing is being assumed or taken for granted. Active listening is most often used to improve personal relationships, reduce misunderstanding and conflicts, strengthen cooperation, and foster understanding.
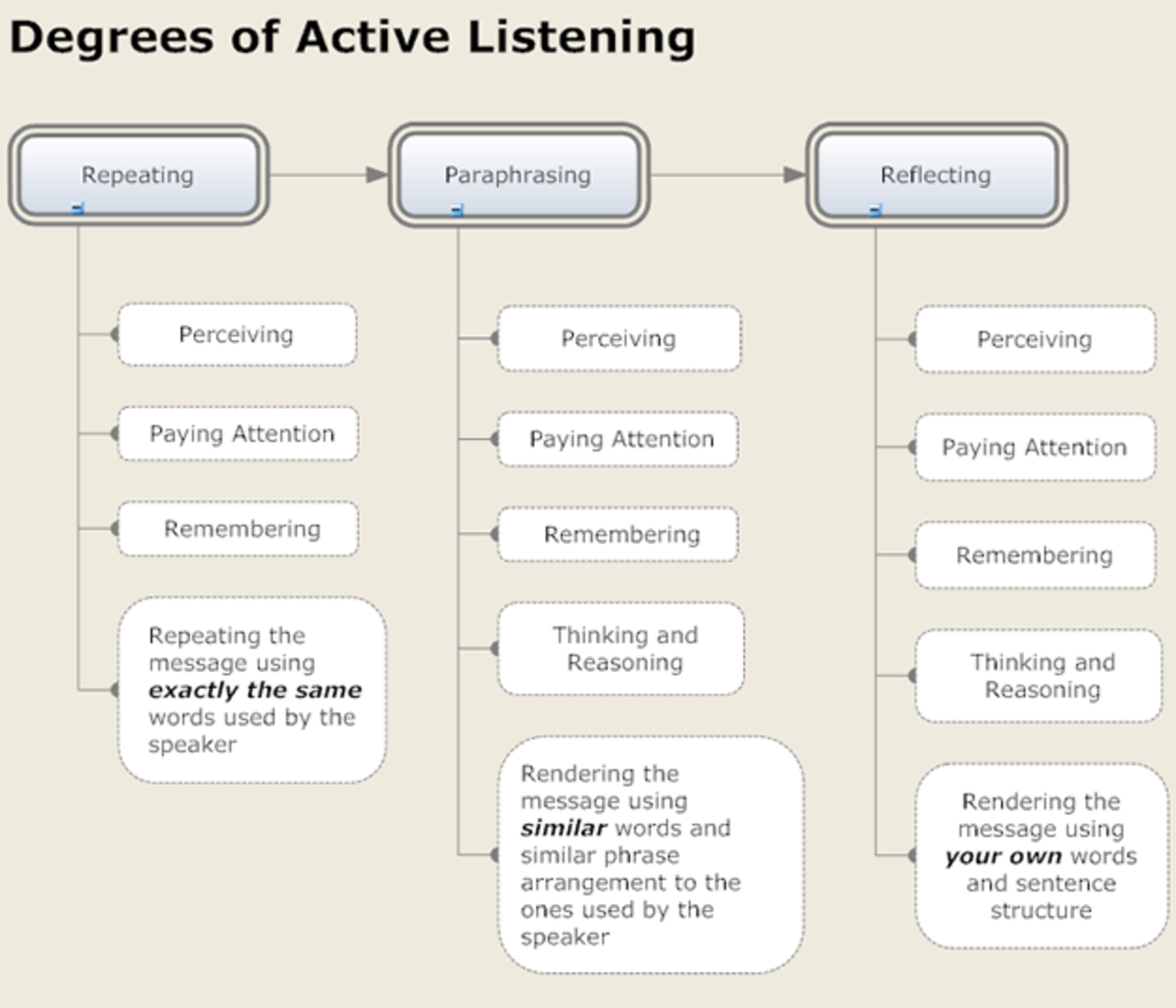
When engaging with a particular speaker, a listener can use several degrees of active listening, each resulting in a different quality of communication with the speaker. This active listening chart shows three main degrees of listening: repeating, paraphrasing, and reflecting.
Active listening can also involve paying attention to the speaker’s behavior and body language. Having the ability to interpret a person’s body language lets the listener develop a more accurate understanding of the speaker’s message.
The Receiving Stage
The first stage of the listening process is the receiving stage, which involves hearing and attending.
Hearing is the physiological process of registering sound waves as they hit the eardrum. As obvious as it may seem, in order to effectively gather information through listening, we must first be able to physically hear what we’re listening to. The clearer the sound, the easier the listening process becomes.
Paired with hearing, attending is the other half of the receiving stage in the listening process. Attending is the process of accurately identifying and interpreting particular sounds we hear as words. The sounds we hear have no meaning until we give them their meaning in context. Listening is an active process that constructs meaning from both verbal and nonverbal messages.
The Challenges of Reception
Listeners are often bombarded with a variety of auditory stimuli all at once, so they must differentiate which of those stimuli are speech sounds and which are not. Effective listening involves being able to focus on speech sounds while disregarding other noise. For instance, a train passenger that hears the captain’s voice over the loudspeaker understands that the captain is speaking, then deciphers what the captain is saying despite other voices in the cabin. Another example is trying to listen to a friend tell a story while walking down a busy street. In order to best listen to what she’s saying, the listener needs to ignore the ambient street sounds.
Attending also involves being able to discern human speech, also known as “speech segmentation. “1 Identifying auditory stimuli as speech but not being able to break those speech sounds down into sentences and words would be a failure of the listening process. Discerning speech segmentation can be a more difficult activity when the listener is faced with an unfamiliar language.
The Understanding Stage
The second stage in the listening process is the understanding stage. Understanding or comprehension occurs when both the speaker and audience share an experience of meaning, and constitutes the first step in the listening process. This is the stage during which the audience determines the context and meanings of the words they hear. Determining the context and meaning of individual words, as well as assigning meaning in language, is essential to understanding sentences, and, thus, both are essential to understanding a speaker’s message.
Once the listener understands the speaker’s main point, they can begin to sort out the rest of the information they are hearing and decide where it belongs in their mental outline. For example, a political candidate listens to her opponent’s arguments to understand what policy decisions that opponent supports.
Before getting the big picture of a message, it can be difficult to focus on what the speaker is saying. Think about walking into a lecture class halfway through. You may immediately understand the words and sentences that you are hearing, but not immediately understand what the lecturer is proving or whether what you’re hearing at the moment is the main point, side note, or digression.
Understanding what we hear is a huge part of our everyday lives, particularly in terms of gathering basic information. In the office, people listen to their superiors for instructions about what they are to do. At school, students listen to teachers to learn new ideas. We listen to political candidates give policy speeches in order to determine who will get our vote. But without understanding what we hear, none of this everyday listening would relay any practical information to us.
One tactic for better understanding a speaker’s meaning is to ask questions. Asking questions allows the listener to fill in any holes he or she may have in the mental reconstruction of the speaker’s message.
The Evaluating Stage
This stage of the listening process is the one during which the listener assesses the information they received, both qualitatively and quantitatively. Evaluating allows the listener to form an opinion of what they heard and, if necessary, to begin developing a response.
During the evaluating stage, the listener determines whether or not the information they heard and understood from the speaker is well constructed or disorganized, biased or unbiased, true or false, significant or insignificant. They also ascertain how and why the speaker has come up with and conveyed the message that they delivered. This process may involve considerations of a speaker’s personal or professional motivations and goals. For example, a listener may determine that a co-worker’s vehement condemnation of another for jamming the copier is factually correct, but may also understand that the co-worker’s child is sick and that may be putting them on edge. A voter who listens to and understands the points made in a political candidate’s stump speech can decide whether those points were convincing enough to earn their vote.
The evaluating stage occurs most effectively once the listener fully understands what the speaker is trying to say. While we can, and sometimes do, form opinions of information and ideas that we don’t fully understand—or even that we misunderstand—doing so is not often ideal in the long run. Having a clear understanding of a speaker’s message allows a listener to evaluate that message without getting bogged down in ambiguities or spending unnecessary time and energy addressing points that may be tangential or otherwise non-essential.
This stage of critical analysis is important for a listener in terms of how what they heard will affect their own ideas, decisions, actions, and/or beliefs.
The Remembering Stage
In the listening process, the remembering stage occurs as the audience categorizes and retains the information they’ve gathered from the speaker for future access. The result—memory—allows the person to record information about people, objects, and events for later recall. This process happens both during and after the speaker’s delivery.
Memory is essential throughout the listening process. We depend on our memory to fill in the blanks when we’re listening and to let us place what we’re hearing at the moment in the context of what we’ve heard before. If, for example, you forgot everything that you heard immediately after you heard it, you would not be able to follow along with what a speaker says, and conversations would be impossible. Moreover, a friend who expresses fear about a dog she sees on the sidewalk ahead can help you recall that the friend began the conversation with her childhood memory of being attacked by a dog.
Remembering previous information is critical to moving forward. Similarly, making associations to past remembered information can help a listener understand what she is currently hearing in a wider context. In listening to a lecture about the symptoms of depression, for example, a listener might make a connection to the description of a character in a novel that she read years before.
Using information immediately after receiving it enhances information retention and lessens the forgetting curve or the rate at which we no longer retain information in our memory. Conversely, retention is lessened when we engage in mindless listening, and little effort is made to understand a speaker’s message.
Because everyone has different memories, the speaker and the listener may attach different meanings to the same statement. In this sense, establishing common ground in terms of context is extremely important, both for listeners and speakers.
The Responding Stage
The responding stage is the stage of the listening process wherein the listener provides verbal and/or nonverbal reactions based on short- or long-term memory. Following the remembering stage, a listener can respond to what they hear either verbally or non-verbally. Nonverbal signals can include gestures such as nodding, making eye contact, tapping a pen, fidgeting, scratching or cocking their head, smiling, rolling their eyes, grimacing, or any other body language. These kinds of responses can be displayed purposefully or involuntarily. Responding verbally might involve asking a question, requesting additional information, redirecting or changing the focus of a conversation, cutting off a speaker, or repeating what a speaker has said back to her in order to verify that the received message matches the intended message.
Nonverbal responses like nodding or eye contact allow the listener to communicate their level of interest without interrupting the speaker, thereby preserving the speaker/listener roles. When a listener responds verbally to what they hear and remember—for example, with a question or a comment—the speaker/listener roles are reversed, at least momentarily.
Responding adds action to the listening process, which would otherwise be an outwardly passive process. Oftentimes, the speaker looks for verbal and nonverbal responses from the listener to determine if and how their message is being understood and/or considered. Based on the listener’s responses, the speaker can choose to either adjust or continue with the delivery of her message. For example, if a listener’s brow is furrowed and their arms are crossed, the speaker may determine that she needs to lighten their tone to better communicate their point. If a listener is smiling and nodding or asking questions, the speaker may feel that the listener is engaged and her message is being communicated effectively.
Conclusion
In short, active listening is crucial for establishing our ethos. If we hope to be persuasive, we need to demonstrate our good will, good character, and good judgement to others by carefully listening and responding to their messages.

