8.1: A Brief History of Public Speaking
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID
- 79282
Learning Objectives
After completing this section, students should be able to:
- explain the relationship between the development of democracy and public speaking.
- identify Aristotle as the author of the three modes of proof.
- differentiate ethos, pathos, and logos.
- explain the tension between content and delivery.
- explain the role of the sophists and how they differed from Aristotle.
- identify Cicero and Quintilian.
- list and define the five canons of rhetoric.
- distinguish between the Humanists and Rationalists
- differentiate the Epistemology Movement, the Belle Lettres Movement, and the Elocutionist Movement.
- identify how radio, television, film, and the internet influenced present-day public speaking.
Since humans have been using language and living in social groups, the act of one person speaking to many has been occurring in some form or other. Whether it was to instruct, to persuade, to motivate, to celebrate, or to mourn, language is the tool humans use to form and maintain social connections.
Even though we know public speaking is as old as language itself, in our Western culture, we typically consider the foundations of our current understanding of public speaking to have been laid in Ancient Greece, more than 2,500 years ago.
In the online, open-source public speaking text found at www.publicspeakingproject.org, Dr. Peter A. DeCaro of the University of Fairbanks, Alaska, lays out the development of public speaking from the Greeks and Romans, through the Renaissance, and into our Modern Period. What follows is a condensed, summarized version of Dr. DeCaro’s work, along with some additional information. For more detail, visit the free online text and review Chapter 2: Origins of Public Speaking.
Public Speaking and Democracy
The development of public speaking as a specific skill is strongly linked to the development of democracy in Ancient Greece. Starting in 621 B.C. in Athens, laws began to convert from an oral tradition heavily controlled by nobility to a written form that could be applied equally and consistently. This codification (creating an organized system of laws) took power from the nobility and moved it into the courts. Assemblies were formed to review, revise, and create laws. Accordingly, there had to be substantive debate and persuasion to reach agreements on how to manage this evolution of legal doctrine, and those coming before the courts needed to engage in public speaking to advocate for their position. Dr. DeCaro states,
In a free society, it is persuasion that decides rules, determines behavior, and acts as the governing agent in human physical and mental activities. In every free society individuals are continuously attempting to change the thoughts and/or actions of others. It is a fundamental concept of a free society.
Democracy demands public speaking as the tool for self-governance. Since being proficient in public speaking was so valuable, the study of how it works likewise became important, emerging as the study of rhetoric.
The Athenian Greeks and Aristotle
Widely considered the founder of the study of rhetoric, Aristotle (384-322 B.C.), Image 1, was the first philosopher to consider the dynamics of public speaking and persuasion, and to compile those observations in The Rhetoric. In effect, this became the first textbook on public speaking. Aristotle defined rhetoric as “all available means of persuasion.” In other words, rhetoric and rhetorical theory refer to the study of techniques for persuasion as they apply to various audiences and occasions.

In his work, Aristotle presented three methods, or “modes,” of persuading an audience. We still consider these Aristotelian modes of proof as the core of how we teach and study persuasion.
Ethos: persuading another based on the character of the speaker. We all have friends or family members we trust, and if they tell us something, we assume they are telling the truth and should be believed. This persuasion by the nature of the speaker’s character is ethos.
A very important aspect of ethos is that credibility is something audience gives the speaker. Since the audience can judge the character of the speaker only on their performance at that moment, the speaker’s credibility is a function of the perception the audience has of that speaker at that time. No matter how trustworthy and honest a speaker is, their credibility is only as strong as the audience believes it to be. Accordingly, speakers need to prove their trustworthiness through their delivery and content. Since this is a standard consideration in the development of a speech introduction, specific methods of enhancing credibility are addressed there.
Pathos: engaging the emotions of the audience. Human beings are deeply emotional creatures, and we are most emotionally comfortable when our beliefs and actions align. If James believes giving to the community is an important activity, that may lead him to donate blood during the college blood drive. He may feel a sense of satisfaction and contentment that his actions and beliefs aligned. On the other hand, if he avoids giving blood, he may feel troubled that his actions are not aligning with his beliefs. This disconnect is at the core of using emotion to persuade.
Humans like feeling positive emotions and don’t like negative emotions. A speaker can offer an audience a way to act that will make them feel good and avoid negative emotion. For example, a famous charity advertisement for Feed the Children claimed, “For the price of a cup of coffee, you can feed a starving child.” This simple statement aims to trigger a sense of guilt each time we buy a cup of coffee, and then offers a way to erase the negative emotion of guilt and replace it with the satisfaction of helping those less fortunate: donate your coffee money to Feed the Children.
Logos: using argument and logical reasoning. While we are deeply emotional creatures, we also place a high value on rational thinking and thoughtful decision making. Through the application of logical reasoning accompanied by credible evidence, we aim to persuade the audience of the best course of action. The study of logic and reasoning are huge fields of study in their own right, and we encourage you to consider additional courses in Logic, Argumentation, or Debate.
Content versus Delivery
During Aristotle’s time, a perpetual tension in the study of public speaking was debated: content versus delivery. For some, the content of the speech is far more important than how that content is presented. Others, however, assert that how the content is presented is as important, if not more important, than the substance of the content. Dr. DeCaro shows that Aristotle was well aware of this distinction: “For Aristotle, rhetoric is the process of developing a persuasive argument, and oratory is the process of delivering that argument.” Aristotle emphasized the rhetorical perspective, while the sophists emphasized the oratorical perspective.
The sophists were traveling instructors who would teach their students persuasive methods, good delivery, and other techniques they could use to advance their position. While the rhetorical emphasis focused on the speaker’s message, the oratorical perspective as taught by the sophists emphasized the speaker’s delivery style. The rhetorical tradition emphasized using rhetoric to find and advance truth, while the oratorical tradition emphasized these skills as a toolkit to be used however the speaker needed to use them.
This tension exists to this day. A criticism occasionally leveled toward a speaker is that of “mere sophistry,” which means the speaker has good style, but the arguments lack conviction and substance, or they are downright deceitful; that the speaker is relying on good delivery without providing substantive content along with it. As you will see, this tension continues even to today in public speaking.
The Romans
After the time of the Athenian Greeks passed and the Roman Republic emerged, two Romans emerged to make significant impacts on the study of rhetoric: Cicero and Quintilian.
Cicero (106-43 B.C.), Image 2, argued for a balance of content and delivery, that “the perfect orator should be able to speakwisely and eloquently on any subject with a dignified, restrained delivery.” He also believed, however, that style without substance was to be avoided. DeCaro states, “Cicero despised the shallowness of orators who depended exclusively on perfect diction and elegant words that lacked substance. His ideal person was the philosopher-statesman-learned orator who used rhetoric to mold public opinion.” Cicero’s importance lies in his writings. DeCaro explains, “His work on rhetoric, the Institutio Oratoria, is an exhaustive volume of twelve books and was a major contribution to education theory and literary criticism.”

Quintilian (35-95 A.D.), Image 3, wrote extensively on speaking, style, and content. He organized what we now know and teach as the five canons of rhetoric:
- Invention: compiling the content of the speech.
- Disposition: arranging the content in an effective order.
- Style: the wording of the presentation.
- Memorization: knowing the presentation and content thoroughly.
- Delivery: the presentation of the content.

Quintilian’s five canons reference both content and delivery, acknowledging that both are important to the success of the persuasion. As Quintilian stated, rhetoric was “the good man speaking well.” In other words, effective public speaking combined substantive, ethical content with good, effective delivery.
The Middle Ages
As the Roman Empire fell and Europe moved into the Middle Ages (400-1400 A.D.), Christianity grew in power and supplanted the human-centered philosophies of the Greeks and Romans. While rhetoric was still considered one of the three great liberal arts during this time, along with logic and grammar, due to Christianity’s distrust of the field, rhetorical theory did not advance significantly during this time. DeCaro states, “As Christianity grew in power, rhetoric was condemned as a pagan art….”
The Renaissance
During the 14th-16th centuries, a revival of interest in classical culture occurred. This renaissance of culture led to a revisiting of the works of the Greeks and Romans, including the works of Aristotle, Cicero, Quintilian, and others. Art, philosophy, literature, and all manner of human endeavor flourished. There was a strong interest in both art and science, with each claiming prominence in discerning truth, justice, and beauty. The humanists believed that language and art could reveal the inner world of the human experience, while the rationalists believed that through science, truth would be revealed. DeCaro states:
Interested in the human world as constructed through language, rather than the natural world, the Humanists focused on human epistemologically. They emphasized the world of human culture and language, believing in the power of the word not only because it gives those with a command of it special advantage in daily interactions, but because of its inherent capacity to disclose to the world of humans.
Poetry, prose, rhetoric, and philosophy were paramount to the humanists as they believed that through the creation and study of these works, truths of the human condition could be discovered. The rationalists, on the other hand, had little regard for such human expression:
Rationalism…sought objective, scientific truths that would exist for all time…. Not surprisingly, the rationalists had little patience for rhetoric: while poetry and oratory might be aesthetically pleasing, they were seen as having no connection to science and truth.
Evidence, logic, and reason were the focus of the rationalists. They felt that through scientific inquiry, the truths of the natural world could be discerned.
1600-1800
During this time, Western Culture began to transition into the political and social structures we have today. Democratic rule began to re-emerge, nobility rule began to wane, and a dispassionate, equitable structure of courts and laws took the place of the rule of the social elites. During this time, as these social and political structures were evolving, new views of public speaking were also emerging.
The Epistemological Tradition
Epistemology is the study of how we know what we know. DaCaro describes it as “the study of the origin, nature, methods, and limits of human knowledge.” The epistemological tradition looked at language as intertwined with human knowledge, perception, and thought. It emphasized the study of how language works, how persuasive appeals work, and the underlying psychology of communication.
The Belles Lettres Movement
The Belle Lettres Movement (meaning “fine or beautiful letters), focused on “the aesthetic qualities of writing rather than any informative value it may have” (DeCaro, ) Great value was placed on beautiful writing and clear wording. In effect, how something was said was more important than the content of the message. This command of language was seen as a reflection of the author’s status and education as well as the reader’s: “Belle-lettres denotes a linguistic self-consciousness testifying to the superior education of both writer and reader, who come together more through literature than through life” (Jehlen and Warner, 1997).
The Elocutionary Movement
The Elocutionary Movement was primarily focused on delivery. The Elocutionists used large, planned gestures, loud and dramatic vocal factors, and exaggerated movements. They believed that carefully planned delivery would have certain effects on the audience, so the emphasis was on finding the “proper” gesture, vocal pattern, or movement appropriate for a specific moment. Later, the Elocutionist Movement became so formulaic that it began to be perceived as fake and insincere.
The Gilded Age
From the mid-1800s to the early 1900s, the ability to speak at length with an ornate style was held in high esteem. Politicians and traveling speakers would go from
town to town delivering long, impassioned speeches on topics of the day. Since there was no mass media, other than newsprint, these were public events that would draw everyone in the community. Without microphones or sound systems, the speakers would use a loud, boisterous style, very much elocutionist in style, to carry their message throughout the audience.

The ability to speak for hours in this style was considered a sign of intelligence and personal power, so speeches not measuring up were considered reflective of a lack of personal strength and character. A good speaker was expected to have a very strong command of language, much in the belles lettres style, and to be able to express himself with a sense of poetry and artistry. Debate was a very highly regarded skill, especially the ability to form well-phrased, targeted arguments. Besting another in an intellectual clash generated much respect.
Present Day Influences
Today, what we consider good public speaking has been altered by several factors from the 20th century. It has been heavily influenced by the introduction of radio, film, television, and the internet.
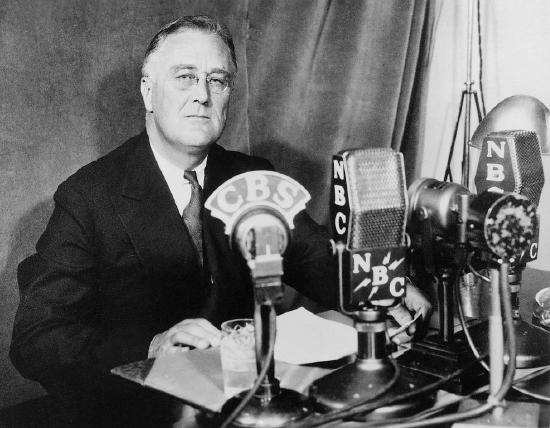

First, radio introduced audiences to the ability to hear a natural voice of political figures in their own home. Most renowned are the “Fireside Chats” of President Franklin Roosevelt. According to History.com, “From March 1933 to June 1944, Roosevelt addressed the American people in some 30 speeches broadcast via radio, speaking on a variety of topics from banking to unemployment to fighting fascism in Europe. Millions of people found comfort and renewed confidence in these speeches, which became known as the “’fireside chats.’” (History.com, 2010) Instead of the loud, projected vocal style needed to fill an auditorium, this new medium allowed a far more intimate, conversational style of presentation.
Second, putting an elocutionist-style speaker, such as William Jennings Bryan, in the close-up view of a movie enhanced the artificial nature of this style of delivery. Since such delivery was intended to reach an audience of several hundred without the aid of a sound system, to now show the speaker’s exaggerated vocal factors, gestures, facial expressions, and body movements up close via film or television made the speaker appear cartoonish by today's standards. Since we can now see speakers up close regardless of the size of the venue, a more natural delivery works more effectively at establishing trust and sincerity.
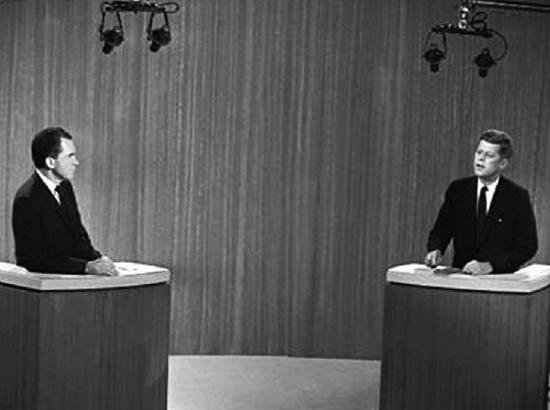
Third, now that we could not only hear but see the speakers, the nonverbal, visual elements of the speaker have become more pronounced. In the 1960 election, U.S. citizens saw the first televised presidential debate between John F. Kenney and Richard M. Nixon. A mark of the impact of this new medium of television is that those who listened via radio felt Nixon won the debate, while those who watched overwhelmingly felt Kennedy won: “Nixon was recovering from a hospital visit and had a 5-o'clock shadow, having refused makeup. In contrast, Kennedy's delivery was smooth and charismatic. Viewers focused on what they saw, not what they heard. Kennedy won the election.” (Newsweek, 2016) Accordingly, “The Kennedy-Nixon debates not only had a major impact on the election’s outcome, but ushered in a new era in which crafting a public image and taking advantage of media exposure became essential ingredients of a successful political campaign.” (History.com 2010) The delivery aspects of public speaking, especially appearance, emerged as a far more crucial element than before.

Fourth, with the emergence of the internet giving us 24/7 access to virtually all the knowledge in the world, speaker’s words can be carefully assessed for accuracy. Instead of taking a speaker at their word, we can check and cross-check the truthfulness of a speaker’s claims in a matter of moments. We have seen the emergence of fact-checking sites that specialize in holding speakers accountable for what they say. Politifact.com, FactCheck.org, and Snopes.com produce assessments daily of current claims by public figures. More than ever, speakers must carefully cite evidence and sources.



Along with accurate citations, speakers must carefully weigh the value of the source itself. Since the internet allows for anyone to publish anything (there are no editors on the internet), speakers must evaluate sources to determine the trustworthiness of the source. We have seen the emergence of political commentators, such as Rush Limbaugh, Alex Jones, Rachel Maddow, or Keith Olbermann, who are advocates for specific viewpoints. We must be cautious of distorted or biased news and opinion, and instead focus on objective, balanced information.
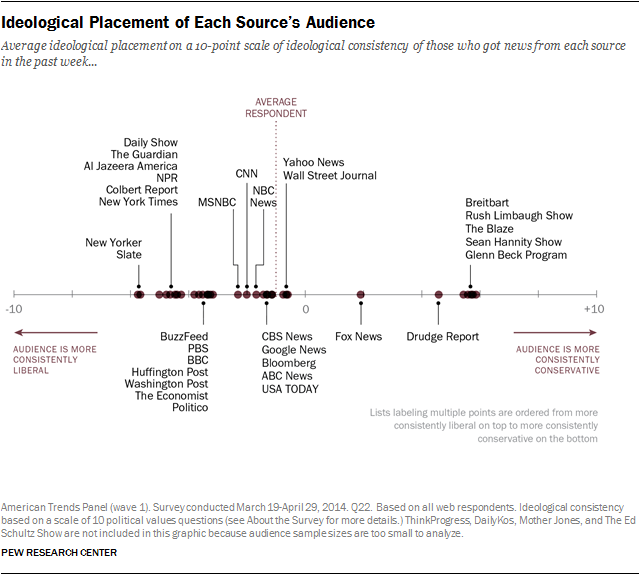
Fifth, in addition to the emergence of the internet is the development of echo chambers fed by partisan, or even hyper-partisan, news and information sites. This means that more than ever different political viewpoints are fed by specific news sources. Typically, sources such as Fox News, The Wall Street Journal, and Nationalreview.com are considered conservative, while MSNBC, Huffington Post, and Salon.com are considered liberal. For us as speakers, it is important we have a sense of what the audience deems most acceptable. To cite Fox News with a liberal audience or MSNBC with a conservative audience may harm the speaker’s credibility. In other words, there are sources some audience members immediately deem biased and lacking credibility, so if we use them, we may have created a barrier with the audience. Instead, to advance our position, we should look for sources that do not carry such pre-existing baggage and are more likely to be seen as credible.
Lastly, another effect of the internet has been little patience for engaging long discourse. Since the virtually infinite web always has something else to look at, we are becoming less and less satisfied with long, detailed presentations. This “Twitter Effect” pushes us to favor short, to-the-point presentations versus longer, exploratory speeches. CNN’s Doug Gross lays out 5 ways that Twitter is altering our relationship with information and how it is presented. He states, “Some thoughts just can't be summed up in 140 characters. For all its ability to provide quick blasts of information, critics have argued that Twitter dumbs down…conversations that deserve to be fuller and more fleshed out.” Accordingly, as speakers we need to be clear, distinct, and avoid rambling. Depending on the audience and occasion, a shorter, more direct presentation may work more effectively than a longer, more detailed speech.

Key Concepts
The terms and concepts students should be familiar with from this section include:
The role of public speaking in democracy
The Athenian Greeks
- Aristotle
- Rhetoric
- Rhetorical Theory
- Ethos
- Pathos
- Logos
- Content versus Delivery
- Sophists
The Romans
- Cicero
- Quintilian
- Invention
- Disposition
- Style
- Memorization
- Delivery
The Middle Ages
The Renaissance
- Humanists
- Rationalists
The Epistemological Tradition
The Belles Lettres Movement
The Elocutionary Movement
The Gilded Age
Present Day Influences
References
Decaro, P.(2011) The origins of public speaking in Public Speaking: The Virtual Text, Retrieved from http://www.publicspeakingproject.org/origins.html
Gross, D. (2011, March 21). 5 Ways Twitter Changed How We Communicate. CNN. Retrieved from www.cnn.com/2011/TECH/social....ion/index.html
The Fireside Chats. (2010). Retrieved from http://www.history.com/topics/fireside-chats
The Kennedy-Nixon Debates. (2010), Retrieved from http://www.history.com/topics/us-pre...-nixon-debates
Jehlen, M, & Warner, M. (1997), The English Literature of America, 1500-1800. New York, NY: Routledge.
Reuters. (2016, September 22). Presidential debates' iconic moments, from Kennedy-Nixon to Obama-Romney. In Newsweek. Retrieved from http://www.newsweek.com/presidential...moments-501670


