Summary
Economics deals with choices. In this chapter we have examined more carefully the range of choices in production that must be made in any economy. In particular, we looked at choices involving the allocation of an economy’s factors of production: labor, capital, and natural resources.
In addition, in any economy, the level of technology plays a key role in determining how productive the factors of production will be. In a market economy, entrepreneurs organize factors of production and act to introduce technological change.
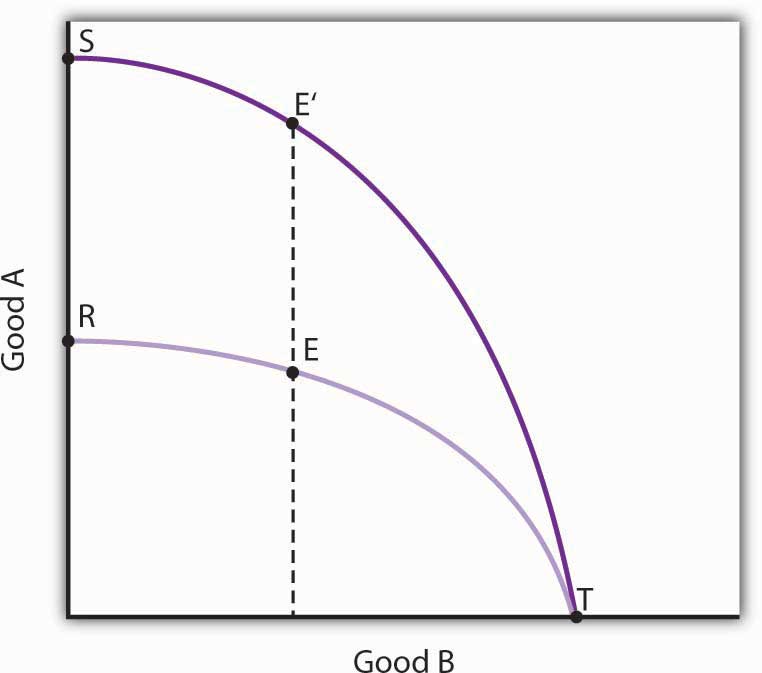
The production possibilities model is a device that assists us in thinking about many of the choices about resource allocation in an economy. The model assumes that the economy has factors of production that are fixed in both quantity and quality. When illustrated graphically, the production possibilities model typically limits our analysis to two goods. Given the economy’s factors of production and technology, the economy can produce various combinations of the two goods. If it uses its factors of production efficiently and has full employment, it will be operating on the production possibilities curve.
Two characteristics of the production possibilities curve are particularly important. First, it is downward sloping. This reflects the scarcity of the factors of production available to the economy; producing more of one good requires giving up some of the other. Second, the curve is bowed out. Another way of saying this is to say that the curve gets steeper as we move from left to right; the absolute value of its slope is increasing. Producing each additional unit of the good on the horizontal axis requires a greater sacrifice of the good on the vertical axis than did the previous units produced. This fact, called the law of increasing opportunity cost, is the inevitable result of efficient choices in production—choices based on comparative advantage.
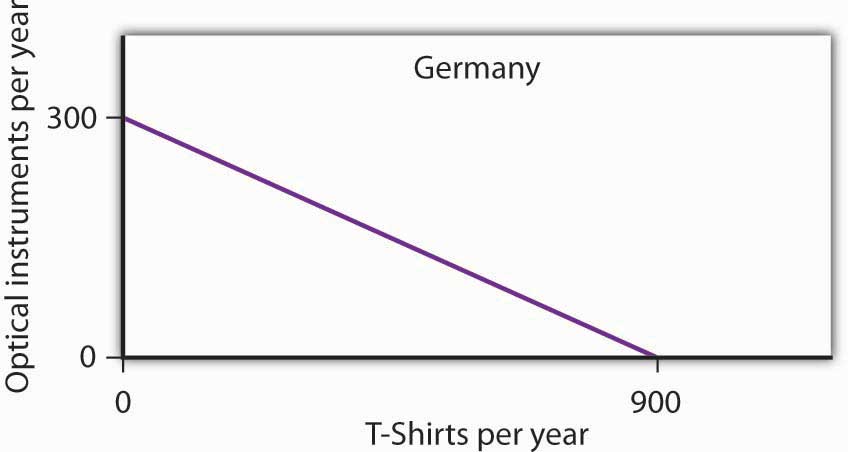
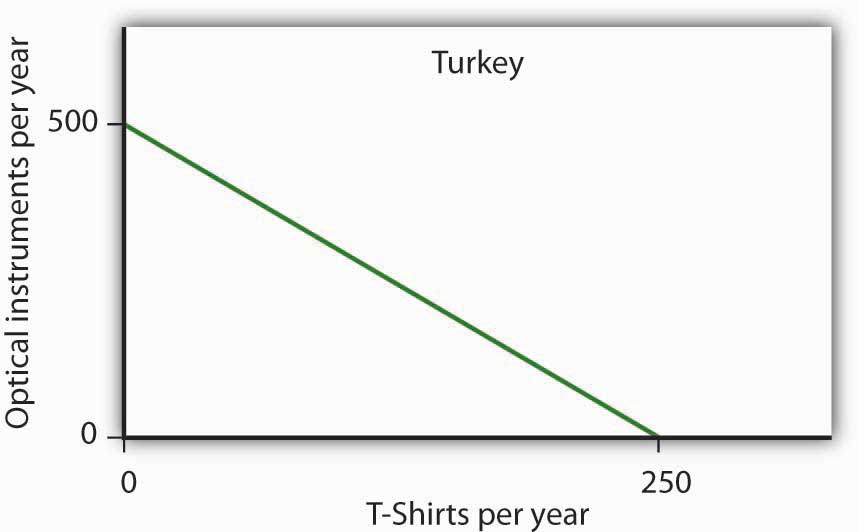
The production possibilities model has important implications for international trade. It suggests that free trade will allow countries to specialize in the production of goods and services in which they have a comparative advantage. This specialization increases the production of all goods and services.
Increasing the quantity or quality of factors of production and/or improving technology will shift the production possibilities curve outward. This process is called economic growth. In the last 50 years, economic growth in the United States has resulted chiefly from increases in human capital and from technological advance.
Choices concerning the use of scarce resources take place within the context of a set of institutional arrangements that define an economic system. The principal distinctions between systems lie in the degree to which ownership of capital and natural resources and decision making authority over scarce resources are held by government or by private individuals. Economic systems include market capitalist, mixed, and command socialist economies. An increasing body of evidence suggests that market capitalist economies tend to be most productive; many command socialist and mixed economies are moving in the direction of market capitalist systems.
The presumption in favor of market-based systems does not preclude a role for government. Government is necessary to provide the system of laws on which market systems are founded. It may also be used to provide certain goods and services, to help individuals in need, and to regulate the actions of individuals and firms.