5.2: Stress and Coping
- Page ID
- 210793
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)5.2: Stress and Coping

It’s 2:00 a.m. and your head is swarming with thoughts, none of them pleasant or relaxing: Did I reply to that important email? Am I ready for the upcoming presentation? Should I have studied more for tomorrow’s test? How long will it take me to fall asleep? Why is this always happening to me? All of these thoughts manifest as stress, an ever-present variable in our lives. You are not alone and as you will find out in this chapter, there are ways of coping and managing these stressors. Furthermore, there are ways that we can help communities better deal with these types of challenges.
WHAT IS STRESS?

So what is stress? This shouldn’t be a trick question, but why is it so hard to answer? Stress can be three things: a stimulus event (i.e., a stressor), a process for understanding the stimulus and its context, and a reaction we have to this event. Essentially, to be stressful the event has to become an overload of incoming information into our system. Stress can cause biological responses such as sweaty palms or a racing heart, as well as psychological responses such as nervousness. It is known to have effects on our behavior causing us to avoid others, and it also affects cognitive performance causing us to have difficulty concentrating.
A number of genetic studies have begun to identify candidate genes that may play a role on diverse forms of stress reactions. It is highly probable that genetics account for some of our responses to stress, but other factors are also of importance. Environmental stressors can also affect our behaviors and emotions. Environmental stressors can be grouped into different types: Major Life Events (e.g., experiencing a breakup, getting married, or having a baby), Life Transitions (e.g., puberty or transition into high school), Daily Hassles (e.g., family arguments or waiting in a long line at a security checkpoint of an airport) and Disasters (e.g., experiencing a car accident or a computer crashing causing loss of important information). These types of environmental stressors can cause you to be fearful and have a racing heartbeat. And our perceptions of these responses can actually make the symptoms worse. It is also important to note that these stressors can be perceived differently by different people. For instance, two people can get stuck in the same elevator and while one would find the experience to be a nuisance, another will tell you it was the worse situation they have ever been in. Here is a poll about the role of stresses and stress responses in the natural world. This supplementary article explores what is the right amount of stress.
PHYSIOLOGICAL VS PSYCHOLOGICAL STRESS
While most of the time we think about stress in a negative way, some stress is adaptive and can even give us an edge. Part of the stress reaction involves the secretion of hormones, which in turn will stimulate the cardiovascular system, which includes your heart. In this way, the right amount of stress may release hormones and increase our ability to focus better on an exam or to quickly maneuver our car when we are trying to avoid an accident. Most stressors in our daily life are psychological in nature—dating, exams, presentations, and deadlines, so the adrenaline and cortisol (i.e., stress hormones) released into the bloodstream do not get burned off. These types of psychological stressors can initiate an over-activation with a tendency to make the stress response worse. So, a response to an environmental stressor may start as fear and turn into a panic attack.
Acute vs Chronic Stress

One of the goals of our body is to maintain stability (i.e., homeostasis). We can, therefore, define stress as an actual or perceived threat capable of throwing our homeostasis off balance. Stress exposure starts the responses. When a person is exposed to prolonged stress, overload may occur. When the stress response is triggered too often and/or remains active too long, it can cause “wear and tear” on the body from lowering your immune system and bone density, to hypertension, to heart attack.
There are two different types of stressors that we typically encounter. Acute stressors are observable stressful events that are time-limited such as an upcoming test or a family gathering. An acute stressor brings activation to our neuroendocrine system and makes us ready to act (i.e., “fight or flight”). Remember that pumped up feeling you got the last time you were getting ready to give a speech in front of the class? Chronic stressors, in contrast, are persistent demands on you; they are typically open-ended, using up your resources in coping but not having any resolution. Here is a short article and podcast on stress effects on health and suggestions for stress preventive activities.
A chronic illness, poverty, and racial discrimination are all examples of chronic stressors. Prolonged stress can lead to an eventual breakdown, such as contributing to aging. A number of recent studies have shown that lower socioeconomic status is associated with higher stress load. In addition, perceptions of racism can serve as a chronic social stressor for ethnic minorities and can, in part, explain some of the health issues of African Americans and other ethnic minority groups in the US and other countries.
Everyday Hassles

Robert Service, a Canadian Poet, cautioned, “Be master of your petty annoyances and conserve your energies for the big, worthwhile things. It isn’t the mountain ahead that wears you out—it’s the grain of sand in your shoe.”
In addition to many stressors in our lives being psychological and chronic in nature, we should pay attention to everyday hassles, which can be as harmful, if not more harmful than life-changing events. Everyday hassles may include things like worrying about one’s weight, having too much work with too little time, or a stressful commute to school or work. Major life changes usually bring about more hassles, which may lead to more physical stress symptoms.
In summary, stress can be adaptive—in a fearful or stress-causing situation, we can run away to save our lives, or we can concentrate better on a test. Biologists might even say it is necessary. But, stress can also be maladaptive. This is especially true if it is prolonged (i.e., chronic stress) because it increases our risk of illness and health problems. Thus, reducing stress, especially prolonged stress, is essential to healthcare. This video explains the effects of daily hassles on our health.
COPING AND STRESS

To deal with stress in your life, it is important to figure out where that stress originates and notice how you tend to react to it. Later in this chapter, we will show you how community psychologists consider the environment and ecological perspectives as intertwined in stress and coping. Lazarus and Folkman (1984) have been among the most influential psychologists in the stress and coping field, and they defined coping as efforts to manage demands that could exceed our resources. It is important to highlight from this definition that when a person perceives a life circumstance as taxing and exceeding the resources they have, this person will experience stress. Therefore, coping involves your efforts to manage stress, which is illustrated in Figure 1.
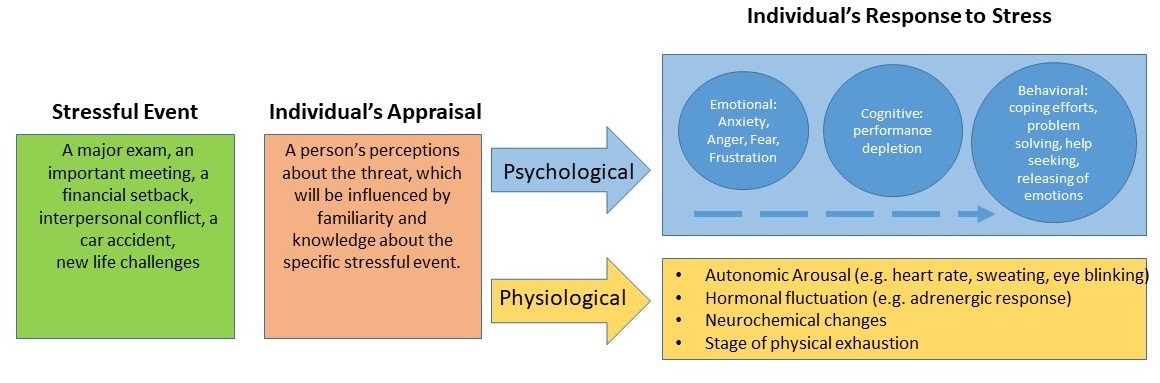 Figure 1. Overview of Stress Process and Coping Responses
Figure 1. Overview of Stress Process and Coping ResponsesCoping Defined
Lazarus and Folkman (1984) felt that when humans perceive a life circumstance as taxing and exceeding their resources, stress will be experienced, which we have already defined in the prior section as an overload of incoming information into a system. Therefore, coping involves persons’ efforts to manage stress, whether the process of dealing with stress is adaptive or not (Lazarus, 1993). When we talk about coping, we will need to consider the intensity of the stressor, the context of coping, and an individual’s appraisal of coping expectations.
Coping Types
Research on coping has usually found five types of coping styles (Clarke, 2006; Skinner, et al., 2003; Folkman & Moskowitz, 2005). These include the following: (1) problem-focused coping style involves addressing the problem situation by taking direct acting, planning or thinking of ways to solve the problem, (2) emotion-focused coping style involves expressing feelings or engaging in emotional release activities such as exercising or practicing meditation, (3) seeking-understanding coping style refers to finding understanding of the problem and looking for a meaning of the experience, and (4) seeking help involves using others as a resource to solve the problem. Finally, people might respond to stressors by (5) avoiding the problem and trying to stay away from the problem or potential solution to the problem.
Coping Strategies
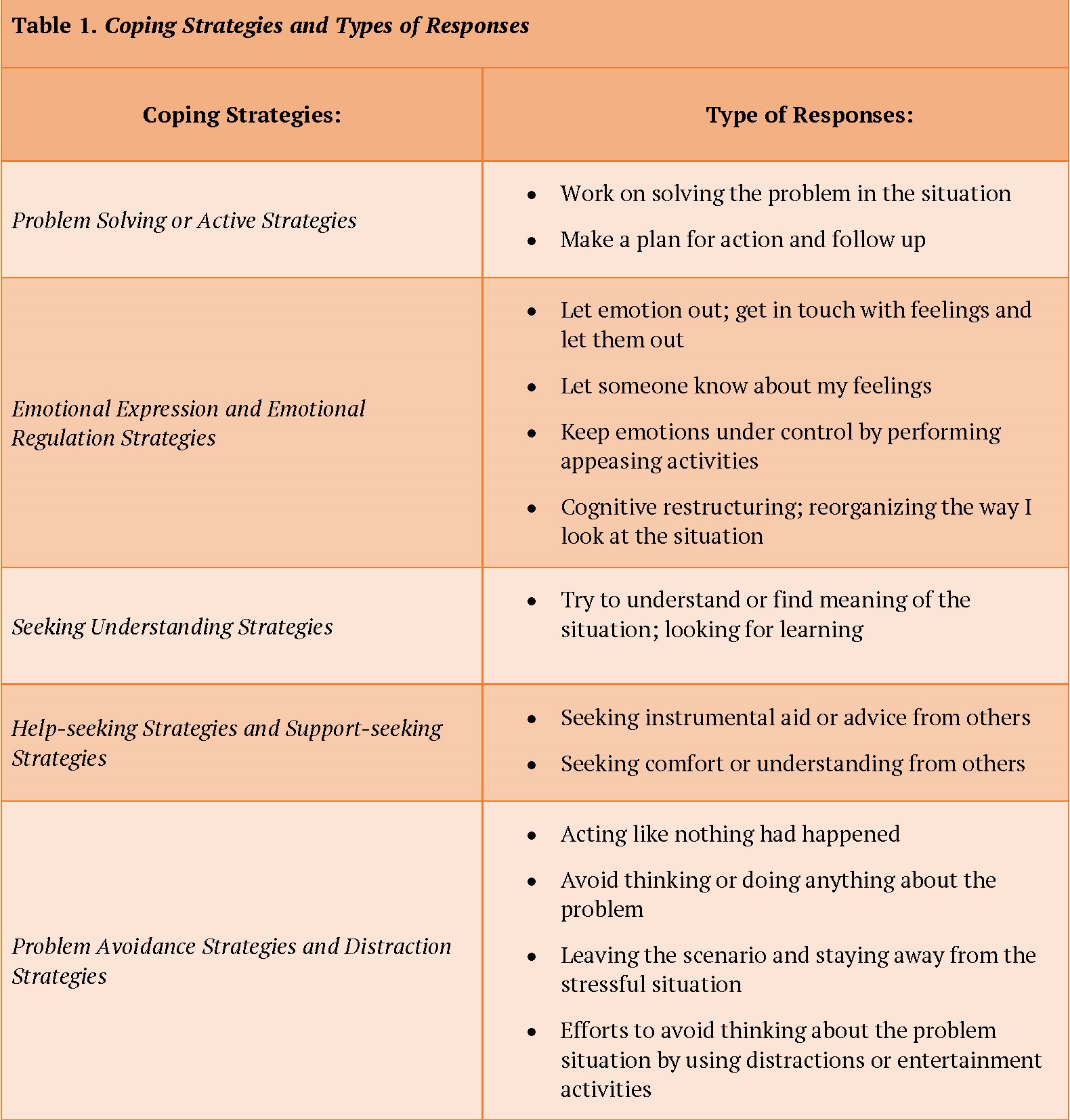
Coping strategies are the choices that a person makes in order to respond to a stressor. A strategy can be adaptive (effective) or maladaptive (ineffective or harmful). The ideal adaptive coping strategy varies depending on the context, as well as the personality traits of the person responding. The coping strategies can be problem-solving or active strategies, emotional expression and regulation strategies, seeking understanding strategies, help or support-seeking strategies, and problem avoidance or distraction strategies.
Here is one example of an intervention strategy that shows how to effectively cope with daily and transitional stressors. The strategy is called Shift-and-Persist (Chen & Miller, 2012), and it requires individuals to first shift views of the problem. To shift, you need to (1) recognize and accept the presence of stress, (2) engage in emotional regulation and control negative emotions, and (3) practice self-distancing from the stressor to gain an outsider’s perspective of the stressful context. To persist, you would need to (1) plan for the future through goal setting, (2) recognize a broader perspective when obstacles arise, (3) determine what brings meaning to your life, and (4) become flexible to determine new pathways to goals. The Center for Disease Control and Prevention and the American Heart Association offer other coping strategies. Two more discussions on coping strategies are found in these two Ted Talk Videos here and here.
Table 1 below presents a list of coping strategies and is a summary of strategies reported in Clarke, 2006; Skinner, et al., 2003; Folkman & Moskowitz, 2005. Although completed lists are more extensive, this table presents styles reported across the three studies that presented similar types of responses.
To understand coping as a process, we need to understand people’s reaction to stress in context. This includes assessing whether the coping thoughts or actions are good or bad for that given challenge and given context. In addition, the process of coping includes the particular person, the particular encounters with the stressor, the time of the person’s reactions, and the outcome being examined.
SUMMING UP

We all experience stress. However, we respond to this stress in different ways. Sometimes low levels of stress can actually be helpful as it could motivate you to study for an exam. Although the experience of stress is very subjective, stress elicits physiological, emotional, and cognitive reactions in us all. To deal with these stressors, we mobilize resources for coping with the problems confronting us. The success of our coping efforts will depend on ourselves as well as the environmental challenge. For example, most of us have the resources to deal with the stress of a thunderstorm, but we might really be challenged if we are confronted with a tornado that comes through our neighborhood. So there are different levels of stressors that we face. In this chapter, we examined the relationship between stressors and coping, we reviewed the different coping styles and the relationship between individual and context and coping outcomes, including resilience. We hope that this review of stress has provided you with some new insights about how you might use a variety of coping strategies to deal with stress and to work toward the reduction of stress among others.
____________________________________________________________________
REFERENCES
Aldrich, D. P., & Meyer, M. A. (2015). Social capital and community resilience. AmericanBehavioral Scientist, 59(2), 254–269. https://doi.org/10.1177/0002764214550299
Barker, G. (2007). Adolescents, social support and help-seeking behavior. An international literature review and programme consultation with recommendations for action. Geneva, Switzerland: Instituto Promundo, Brazil.
Chen, E., & Miller, G. E. (2012). “Shift-and-Persist” strategies: Why low socioeconomic status isn’t always bad for health. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 7(2), 135-158.
Clarke, A. T. (2006). Coping with interpersonal stress and psychosocial health among children and adolescents: A meta-analysis. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 35(1), 11-24.
Folkman, S., & Moskowitz, J. T. (2005). Coping: Pitfalls and promise. Annual Review of Psychology, 55, 745-774.
Garmezy, N. (1974). Children at risk: The search for the antecedents of schizophrenia. Part I. Conceptual model and research methods. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 1(8), 14- 90.
Jason, L.A., Glantsman, O., O’Brien, J. F., & Ramian, K. N. (2019). Introduction to the field of Community Psychology. In L. A. Jason, O. Glantsman, J. F. O’Brien, & K. N. Ramian (Eds.), Introduction to Community Psychology: Becoming an agent of change. Retrieved from https://press.rebus.community/introd...ty-psychology/
Jason, L. A., & Burrows, B. (1983). Transition training for high school seniors. CognitiveTherapy and Research, 7(1), 79-92.
Luthar, S. S., Crossman, E. J., & Small, P. J. (2015). Resilience and adversity. In R. M. Lerner, & M. E. Lamb (Eds.), Handbook of Child Psychology and Developmental Science (7th ed., Vol. 3, pp. 247-286). New York, NY: Wiley.
Lawlor, J. A., Hunter, B. A., Jason. L. A., & Rosing, H. B. (2014). Natural mentoring in Oxford House recovery homes: A preliminary analysis. Journal of Groups in Addiction Recovery, 52, 126–142.
Lazarus, R. S. (1993) Coping theory and research: Past, present, and future. Psychometric Medicine, 55, 234-247.
Lazarus, R. S., & Folkman, S. (1984). Stress, Appraisal, and Coping. New York: Springer.
Masten, A. S. (2001). Ordinary magic: Resilience processes in development. American Psychologist, 56, 227-238.
Patel, S. S., Rogers, M. B., Amlôt, R., & Rubin, G. J. (2017). What do we mean by ‘community resilience’? A systematic literature review of how it is defined in the literature. PLoS currents, 9, ecurrents.dis.db775aff25efc5ac4f0660ad9c9f7db2.
Wright M. O., Masten A. S., & Narayan A. J. (2013). Resilience processes in development: Four waves of research on positive adaptation in the context of adversity. In S. Goldstein, & R. Brooks (Eds.), Handbook of Resilience in Children. Springer, Boston, MA
Skinner E. A., Edge, K., Altman, J., & Sherwood, H. (2003). Searching for the structure of coping: A Review and critique of category systems for classifying ways of coping. Psychological Bulletin, 129(2), 216-269.
Werner, E. E. (1996). How children become resilient: Observations and causations. Resiliency inAction, 1(1), 18-28.
5.2: Stress and Coping is shared under a not declared license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts.

