3.10: Chromosomal Structural Rearrangements
- Page ID
- 62210
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
Cytologists have characterized numerous structural rearrangements in chromosomes, but chromosome inversions and translocations are the most common. Both are identified during meiosis by the adaptive pairing of rearranged chromosomes with their former homologs to maintain appropriate gene alignment. If the genes carried on two homologs are not oriented correctly, a recombination event could result in the loss of genes from one chromosome and the gain of genes on the other. This would produce aneuploid gametes.
Chromosome Inversions
A chromosome inversion is the detachment, 180° rotation, and reinsertion of part of a chromosome. Inversions may occur in nature as a result of mechanical shear, or from the action of transposable elements (special DNA sequences capable of facilitating the rearrangement of chromosome segments with the help of enzymes that cut and paste DNA sequences). Unless they disrupt a gene sequence, inversions only change the orientation of genes and are likely to have more mild effects than aneuploid errors. However, altered gene orientation can result in functional changes because regulators of gene expression could be moved out of position with respect to their targets, causing aberrant levels of gene products.

An inversion can be pericentric and include the centromere, or paracentric and occur outside of the centromere (Figure). A pericentric inversion that is asymmetric about the centromere can change the relative lengths of the chromosome arms, making these inversions easily identifiable.
- Pericentric inversions include the centromere, and paracentric inversions do not.
- A pericentric inversion can change the relative lengths of the chromosome arms; a paracentric inversion cannot.
When one homologous chromosome undergoes an inversion but the other does not, the individual is described as an inversion heterozygote. To maintain point-for-point synapsis during meiosis, one homolog must form a loop, and the other homolog must mold around it. Although this topology can ensure that the genes are correctly aligned, it also forces the homologs to stretch and can be associated with regions of imprecise synapsis.

When one chromosome undergoes an inversion but the other does not, one chromosome must form an inverted loop to retain point-for-point interaction during synapsis. This inversion pairing is essential to maintaining gene alignment during meiosis and to allow for recombination.
Translocations
A translocation occurs when a segment of a chromosome dissociates and reattaches to a different, nonhomologous chromosome. Translocations can be benign or have devastating effects depending on how the positions of genes are altered with respect to regulatory sequences. Notably, specific translocations have been associated with several cancers and with schizophrenia. Reciprocal translocations result from the exchange of chromosome segments between two nonhomologous chromosomes such that there is no gain or loss of genetic information.

A reciprocal translocation occurs when a segment of DNA is transferred from one chromosome to another, nonhomologous chromosome. (credit: modification of work by National Human Genome Research/USA)
One form of sympatric speciation can begin with a serious chromosomal error during cell division. In a normal cell division event chromosomes replicate, pair up, and then separate so that each new cell has the same number of chromosomes. However, sometimes the pairs separate and the end cell product has too many or too few individual chromosomes in a condition called aneuploidy (see below).

Which is most likely to survive, offspring with 2n+1 chromosomes or offspring with 2n-1 chromosomes? It is always better to have too much information than too little. The cells with 2n+1 (trisomy) are more likely to survive. The cells with 2m-1 (monosomy) would not survive. If a trisomy cell is fertilized, this could lead to the offspring having 47 chromosomes instead of 46. An example is Down Syndrome (Trisomy 21).
Polyploidy is a condition in which a cell or organism has an extra set, or sets, of chromosomes. Scientists have identified two main types of polyploidy that can lead to reproductive isolation of an individual in the polyploidy state. Reproductive isolation is the inability to interbreed. In some cases, a polyploid individual will have two or more complete sets of chromosomes from its own species in a condition called autopolyploidy. The prefix “auto-” means “self,” so the term means multiple chromosomes from one’s own species. Polyploidy results from an error in meiosis in which all of the chromosomes move into one cell instead of separating.
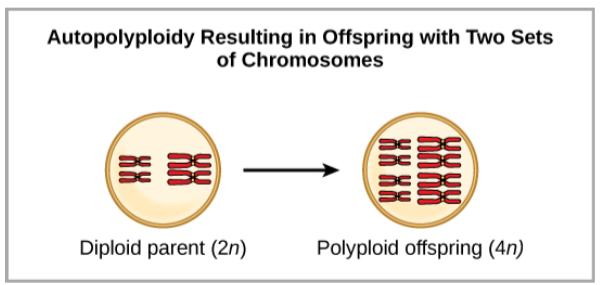
Autopolyploidy results when mitosis is not followed by cytokinesis. For example, if a plant species with 2n = 6 produces autopolyploid gametes that are also diploid (2n = 6, when they should be n = 3), the gametes now have twice as many chromosomes as they should have. These new gametes will be incompatible with the normal gametes produced by this plant species. However, they could either self-pollinate or reproduce with other autopolyploid plants with gametes having the same diploid number. In this way, sympatric speciation can occur quickly by forming offspring with 4n called a tetraploid. These individuals would immediately be able to reproduce only with those of this new kind and not those of the ancestral species.

