5.1: Importance of Nonverbal Communication in Interaction
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID
- 115942

- Jason S. Wrench, Narissra M. Punyanunt-Carter & Katherine S. Thweatt
- SUNY New Paltz & SUNY Oswego via OpenSUNY
Learning Outcomes
- Understand the importance of nonverbal communication.
- Differentiate between the functions of nonverbal communication.
- Understand the functions of nonverbal communication in day-to-day interactions.
- Understand and provide examples of the subcategories of nonverbal communication.
Earlier in this book, we introduced the concept of “you cannot, not communicate.” The foundation for this idea is that even though we may not be sending verbal messages, we are continually sending nonverbal messages. As such, it’s very important to understand how nonverbal messages impact our daily interpersonal interactions. In this section, we’re going to discuss the role that nonverbal communication plays in our daily lives and the six functions of nonverbal communication.
The Role of Nonverbal in Everyday Life
We communicate nonverbally constantly. It’s the primary way that we communicate with other people. In this section, we’re going to explore the role that nonverbal communication plays in our day-to-day lives.
Nonverbal has Communicative Value
The meaning associated with nonverbal communication in any given interaction cannot be underestimated. In this chapter, you will learn about the many types of nonverbal communication present in the interaction. For example, if you are having a conversation with your friend who just broke up with her girlfriend, you will use more than the words, “I just broke up with my girlfriend” to understand how to communicate with your friend. Your friend’s facial expression, way of standing, rate of speech, tone of voice, and general appearance, just to name a few, will indicate to you how you should respond. If she is sobbing, gasping for air, hunched over, and appears emotionally pained, you might attempt to comfort her. If she says, “I just broke up with my girlfriend” and sighs while placing her hand over her heart, she might appear relieved. Your response might be, “it seems like you may be a little relieved. Were things not going well?”
Thus, nonverbal communication plays a tremendous role in successfully engaging in interactions. The successful use of nonverbal communication requires an awareness of the value of nonverbal communication and the belief that it is valuable. When individuals are unaware of the importance of nonverbal communication, they may be overlooking crucial interactional information. For example, one of the authors of this textbook was once meeting with a colleague who was repeatedly sighing during a meeting. Later, when she and her colleague were discussing the meeting, he said, “Didn’t you notice that I was sighing?” She told him she did notice that he was sighing, but she was unsure why. We will discuss this further in the ambiguity of nonverbal communication. In this example, the author’s colleague was aware of the importance of nonverbal communication and attempted to use it deliberately.
In addition to awareness, individuals must believe that nonverbal communication is valuable. If your parent/guardian ever said to you, “it wasn’t what you said, it was how you said it,” then your parent/ guardian was demonstrating a belief that nonverbal communication is essential. An individual may acknowledge that nonverbal communication exists but may discount its value. For example, one of the authors had a recurring argument with the author’s spouse, who would sigh or roll her eyes as a response in interaction. The author would ask the spouse what it meant, and the spouse would inevitably say, “I can sigh or roll my eyes without it meaning anything.” This is not an uncommon response, but the authors of this text hope to dispel this perception.
For a better understanding of the value of communication, Google “value of communication.” Your search will return over a billion links. While it is not possible to review all of the search results, read through a few of the articles. For this exercise we found titles like “The Value of Effective Communication in the Workplace” a and “Why Communication Is Today’s Most Important Skill.” 2 In fact, we found almost 300,000 articles with the phrase “value of communication.” These news articles tell readers that effective communication secures customer, creates bonds between employees, and increases revenues.
Nonverbal Used for Relational Purposes
Nonverbal communication is an essential element in relating to others. Nonverbal communication is often the very first way in which we invite a relationship with another, or, at the very least, invite communication. To communicate with another, we must make eye contact with a few exceptions. Thus, relationships begin with nonverbal communication. Also, consider how humans relate to others through touch, scent, hand gestures, physical appearance, and more.
Humans often use nonverbal communication to relay to others an interest in continuing a conversation or leaving a conversation. For example, you may run into a colleague and strike up a spontaneous conversation in the hall. The conversation is enjoyable, and you each relate to the other that you are enjoying conversing about work. Your colleague may recognize that he needs to get to a meeting and relates this information to you by looking at his watch, beginning to back away, or looking at the door he needs to enter.
Another way in which we relate to others via nonverbal communication is through the communication of emotion. Through a myriad of nonverbal behaviors, we can communicate emotions such as joy, happiness, and sadness. The nonverbal expression of emotion allows others to know how to communicate with us.
Nonverbal is Ambiguous
A particularly challenging aspect of nonverbal communication is the fact that it is ambiguous. In the seventies, nonverbal communication as a topic was trendy. Some were under the impression that we could use nonverbal communication to “read others like a book.” One of the authors remembers her cousin’s wife telling her that she shouldn’t cross her arms because it signaled to others that she was closed off. It would be wonderful if crossing one’s arms signaled one meaning, but think about the many meanings of crossing one’s arms. An individual may have crossed arms because the individual is cold, upset, sad, or angry. It is impossible to know unless a conversation is paired with nonverbal behavior.
Another great example of ambiguous nonverbal behavior is flirting! Consider some very stereotypical behavior of flirting (e.g., smiling, laughing, a light touch on the arm, or prolonged eye contact). Each of these behaviors signals interest to others. The question is whether an individual engaging in these behaviors is indicating romantic interest or a desire for platonic friendship…have you ever walked away from a situation and explained a person’s behavior to another friend to determine whether you were being flirted with? If so, you have undoubtedly experienced the ambiguity of nonverbal communication.
Nonverbal is Culturally Based
Just as we have discussed that it is beneficial to recognize the value of nonverbal communication, we must also acknowledge that nonverbal communication is culturally based. Successful interactions with individuals from other cultures are partially based on the ability to adapt to or understand the nonverbal behaviors associated with different cultures. There are two aspects to understanding that nonverbal communication is culturally based. The first aspect is recognizing that even if we do not know the appropriate nonverbal communication with someone from another culture, then we must at least acknowledge that there is a need to be flexible, not react, and ask questions. The second aspect is recognizing that there are specific aspects of nonverbal communication that differ depending on the culture. When entering a new culture, we must learn the rules of the culture.
Regarding recognizing differences, you may encounter someone from a culture that communicates very differently from you and perhaps in an unexpected way. For example, one of the author’s brothers, Patrick, was working in Afghanistan as a contractor on a military base. He was working with a man from Africa. During their first conversation, he held Patrick’s hand. Patrick later told his sister, the author, this story and said he wasn’t sure how to respond, so he “just rolled with it.” Patrick’s response allowed for the most flexibility in the situation and the best chance of moving forward productively. Imagine if he had withdrawn his hand quickly with a surprised look on his face. The outcome of the interaction would have been very different.
Patrick’s response also exemplifies the second aspect of understanding that nonverbal communication is culturally based. Patrick was hired by a contractor to work on the military base in Afghanistan. The contracting firm could have trained Patrick and his coworkers about communicating with the various cultures they would encounter on the base. For example, many people from the Philippines were working on the base. It would have been helpful for the contractors to explain that there may be differences in spatial distance and touch when communicating with other males from the Philippines. Researching and understanding the nonverbal communication of different countries before entering the country can often mean a smoother entry phase, whether conducting business or simply visiting.
Attribution Error
A final area to address before examining specific aspects of nonverbal communication is “attribution error.” Attribution error is defined as the tendency to explain another individual’s behavior in relation to the individual’s internal tendencies rather than an external factor. 3 For example, if a friend is late, we might attribute this failure to be on time as the friend being irresponsible rather than running through a list of external factors that may have influenced the friend’s ability to be on time such as an emergency, traffic, read the time wrong, etc. It is easy to make an error when trying to attribute meaning to the behaviors of others, and nonverbal communication is particularly vulnerable to attribution error.
On Saturday, September 8, 2018, Serena Williams may have been a victim of an umpire’s attribution error on the part of the judge. Let’s just say Serena did suffer as a result of attribution error. The judge spotted Serena Williams’ coach gesturing in the audience and assumed that the gesture was explicitly directed toward Serena as a means to coach her. Her coach later acknowledged that he was “coaching” via nonverbal signals, but Serena was not looking at him, nor was she intended to be a recipient. Her coach indicated that all coaches gesture while sitting in the stands as though they are coaching a practice and that it’s a habit and not an other-oriented communication behavior. This is a perfect example of attribution error. The judge attributed the coaches’ gesture to the coach intending to communicate rather than the gesture merely being due to habit. The judge’s attribution error may have cost Serena William’s comeback match. While the stakes may not be so high in day-to-day interaction, attribution error can create relational strife and general misunderstandings that can be avoided if we recognize that it is necessary to understand the intention behind a specific nonverbal behavior.
Omnipresent
According to Dictionary.com, omnipresent is indicative of being everywhere at the same time. Nonverbal communication is always present. Silence is an excellent example of nonverbal communication being omnipresent. Have you ever given someone the “silent treatment?” If so, you understand that by remaining silent, you are trying to convey some meaning, such as “You hurt me” or “I’m really upset with you.” Thus, silence makes nonverbal communication omnipresent
Another way of considering the omnipresence of nonverbal communication is to consider the way we walk, posture, engage in facial expression, eye contact, lack of eye contact, gestures, etc. When sitting alone in the library working, your posture may be communicating something to others. If you need to focus and don’t want to invite communication, you may keep your head down and avoid eye contact. Suppose you are walking across campus at a brisk pace. What might your pace be communicating?
When discussing the omnipresence of nonverbal communication, it is necessary to discuss Paul Watzlawick’s assertion that humans cannot, not communicate. This assertion is the first axiom of his interactional view of communication. According to Watzlawick, humans are always communicating. As discussed in the “silent treatment” example and the posture and walking example, communication is found in everyday behaviors that are common to all humans. We might conclude that humans cannot escape communicating meaning.
Can Form Universal Language
When discussing whether nonverbal communication is a universal language, caution must be used. We must remember that understanding the context in which nonverbal communication is used is almost always necessary to understand the meaning of nonverbal communication. However, there are exceptions concerning what Paul Ekman calls “basic emotions.” These will be discussed a bit later in the chapter.
Can Lead to Misunderstandings
Comedian Samuel J. Comroe has tremendous expertise in explaining how nonverbal communication can be misunderstood. Comroe’s comedic routines focus on how Tourette’s syndrome affects his daily living. Tourette’s syndrome can change individual behavior, from uncontrolled body movements to uncontrolled vocalizations. Comroe often appears to be winking when he is not. He explains how his “wink” can cause others to believe he is joking when he isn’t. He also tells the story of how he met his wife in high school. During a skit, he played a criminal and she played a police officer. She told him to “freeze,” and he continued to move (due to Tourette’s). She misunderstood his movement to mean he was being defiant and thus “took him down.” You can watch Comroe’s routine here.
Although nonverbal misunderstandings can be humorous, these misunderstandings can affect interpersonal as well as professional relationships. One of the authors once went on an important job interview for a job she was not offered. She asked the interviewer for feedback, and he said, “your answers sounded canned.” The author did not think to do so in the moment, but what she should have said is that she may have sounded canned because she frequently thinks about work, her work philosophy, and how she approaches work. Thus, her tone may have been more indicative of simply knowing how she feels rather than “canned.”
As you continue to learn about nonverbal communication, consider how you come to understand nonverbal communication in interactions. Sometimes, the meaning of nonverbal communication can be fairly obvious. Most of the time a head nod in conversation means something positive such as agreement, “yes,” keep talking, etc. At other times, the meaning of nonverbal communication isn’t clear. Have you ever asked a friend, “did she sound rude to you” about a customer service representative? If so, you are familiar with the ambiguity of nonverbal communication.
Usually Trusted
Despite the pitfalls of nonverbal communication, individuals typically rely on nonverbal communication to understand the meaning in interactions. Communication scholars agree that the majority of meaning in any interaction is attributable to nonverbal communication. It isn’t necessarily true, but we are taught from a very early age that lack of eye contact is indicative of lying. We have learned through research that this “myth” is not necessarily true; this myth does tell a story about how our culture views nonverbal communication. That view is simply that nonverbal communication is important and that it has meaning.
Another excellent example of nonverbal communication being trusted may be related to a scenario many have experienced. At times, children, adolescents, and teenagers will be required by their parents/ guardians to say, “I’m sorry” to a sibling or the parent/guardian. Alternatively, you may have said “yes” to your parents/guardians, but your parent/guardian doesn’t believe you. A parent/guardian might say in either of these scenarios, “it wasn’t what you said, it was how you said it.” Thus, we find yet another example of nonverbal communication being the “go-to” for meaning in an interaction.
According to research, as much as 93% of meaning in any interaction is attributable to nonverbal. communication. Albert Mehrabian asserts that this 93% of meaning can be broken into three parts (Figure 5.1.1) 4
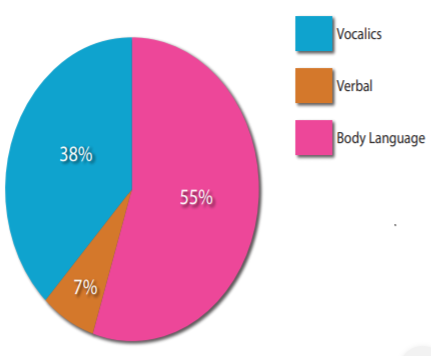
Mehrabian’s work is widely reported and accepted. Other researchers Birdwhistell and Philpott say that meaning attributed to nonverbal communication in interactions ranges from 60 to 70%.5,6 Regardless of the actual percentage, it is worth noting that the majority of meaning in interaction is deduced from nonverbal communication.
The Six Functions of Nonverbal Communication
As we have established, nonverbal communication plays an important role in communicating successfully and effectively. Because nonverbal communication plays a significant role in interactions, nonverbal communication was studied heavily in the early days of studying communication. These studies resulted in the discovery of multiple utilitarian functions of nonverbal communication (Figure 5.1.2)
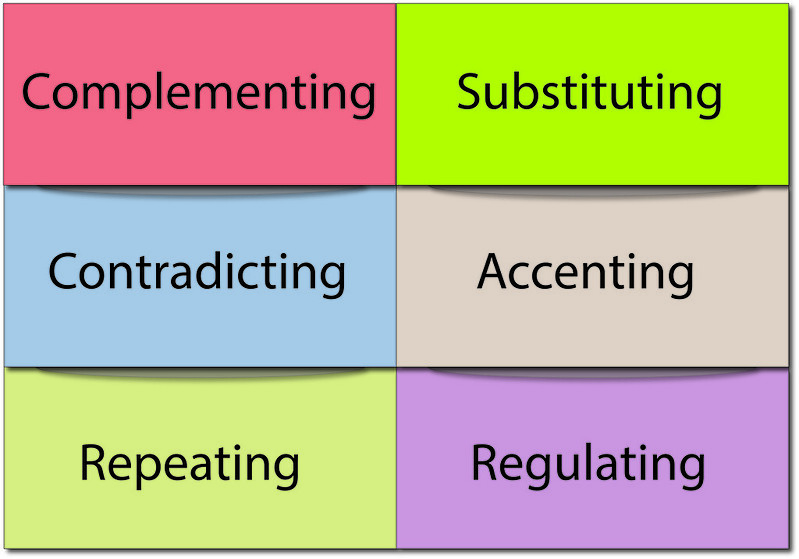
Complementing
Complementing is defined as nonverbal behavior that is used in combination with the verbal portion of the message to emphasize the meaning of the entire message. An excellent example of complementing behavior is when a child is exclaiming, “I’m so excited” while jumping up and down. The child’s body is further emphasizing the meaning of “I’m so excited.”
Contradicting
At times, an individual’s nonverbal communication contradicts verbal communication. Recently, when visiting an aunt’s house, one of the author’s folded her arms. She asked the author if she was cold and if she needed to turn up the air conditioning. The author said no because she was trying to be polite, but her aunt did not believe her. The author’s nonverbal communication gave away her actual discomfort! In this case, the nonverbal communication was truly more meaningful than verbal communication.
Consider a situation where a friend says, “The concert was amazing,” but the friend’s voice is monotone. A response might be, “oh, you sound real enthused.” Communication scholars refer to this as “contradicting” verbal and nonverbal behavior. When contradicting occurs, the verbal and nonverbal messages are incongruent. This incongruence heightens our awareness, and we tend to believe the nonverbal communication over verbal communication.
Accenting
Accenting is a form of nonverbal communication that emphasizes a word or a part of a message. The word or part of the message accented might change the meaning of the message. Accenting can be accomplished through multiple types of nonverbal behaviors. Gestures paired with a word can provide emphasis, such as when an individual says, “no (slams hand on table), you don’t understand me.” By slamming the hand on a table while saying “no,” the source draws attention to the word. Words or phrases can also be emphasized via pauses. Speakers will often pause before saying something important. Your professors likely pause just before relaying information that is important to the course content.
Repeating
Nonverbal communication that repeats the meaning of verbal communication assists the receiver by reinforcing the words of the sender. Nonverbal communication that repeats verbal communication may stand alone, but when paired with verbal communication, it servers to repeat the message. For example, nodding one’s head while saying “yes” serves to reinforce the meaning of the word “yes,” and the word “yes” reinforces the head nod.
Regulating
Regulating the flow of communication is often accomplished through nonverbal behavior communication. Paul Ekman and Wallace Friesen state that regulators are “acts which maintain and regulate the back-and-forth nature of speaking and listening between two or more interactions” (1969, p. 82). You may notice your friends nodding their heads when you are speaking. Nodding one’s head is a primary means of regulating communication. Other behaviors that regulate conversational flow are eye contact, moving or leaning forward, changing posture, and eyebrow raises, to name a few. You may also have noticed several nonverbal behaviors people engage in when trying to exit a conversation. These behaviors include stepping away from the speaker, checking one’s watch/phone for the time, or packing up belongings. These are referred to as leave-taking behaviors. Without the regulating function of nonverbal behaviors, it would be necessary to interrupt conversational content to insert phrases such as “I have to leave.” However, when interactants fail to recognize regulating behavior, verbal communication will be used instead.
Substituting
At times, nonverbal behavior serves to replace verbal communication altogether. Substituting nonverbal behaviors must be understood within a context more often than not. For example, a friend may ask you what time it is, and you may shrug your shoulders to indicate you don’t know. At other times, your friend may ask whether you want pizza or sushi for dinner, and you may shrug your shoulders to indicate you don’t care or have no preference.
Emblems are a specific type of substituting nonverbal behavior that have direct verbal translation. Emblems may generally be understood outside of the context in which they are used. Some highly recognizable emblems in the U.S. culture are the peace sign and the okay sign. Emblems are a generally understood concept and have made their way into popular culture. The term “emblem” may not be applied within popular culture. In the popular television show, Friends, the main characters Ross and Monica are siblings. Ross and Monica are forbidden to “flip the bird” to each other, so they make up their own “emblem,” which involves holding one’s palms upward in a fist and bumping the outside of the palm’s together. Whether flipping the bird in the traditional manner or doing so Ross and Monica style, each of these represents an emblem that does not require context for accurate interpretation. Emblems will be discussed in greater depth later in the chapter.
Key Takeaways
- Nonverbal cues help the receiver decode verbal messages.
- Each function of nonverbal communication is distinct.
- The functions of nonverbal communication are evident in everyday interactions.
Exercises
- Create a list of five situations in which nonverbal communication helped you to accurately interpret verbal communication. Use the functions of nonverbal communication in your description.
- Reflect upon the functions of nonverbal communication and provide an example from your own life for each function.
- Experiment with nonverbal communication. Use an unexpected nonverbal cue when having conversations with friends throughout the day. For example, use a contradictory nonverbal cue such as shaking your head while saying yes. Note your friend’s reaction and be ready to provide an explanation to your friend.

