4.10: Summary
- Page ID
- 58093
As educators increasingly encounter students with complex academic, social, and emotional needs, it is imperative they have research-based tools that can be appropriately and effectively utilized in unique contexts. The research on the effectiveness of function-based supports is vast, but educators are often missing the “how to” or “practical” strategies drawn from research. This chapter highlights “scaled-down” research-based critical features to consider when developing a function-based behavior support plan. It illustrates the importance of utilizing the function of a student’s behavior to outline prevention, teaching, and consequence strategies synergistically to positively impact student outcomes. As a reference, a list of essential components of behavior interventions presented in the chapter is provided in Figures 4.10.1 and 4. Finally, possible antecedent, behavioral teaching, and consequence strategies are presented for the functions of obtaining attention (Table 4.10.1) and escaping tasks or stimuli (Table 4.10.2).
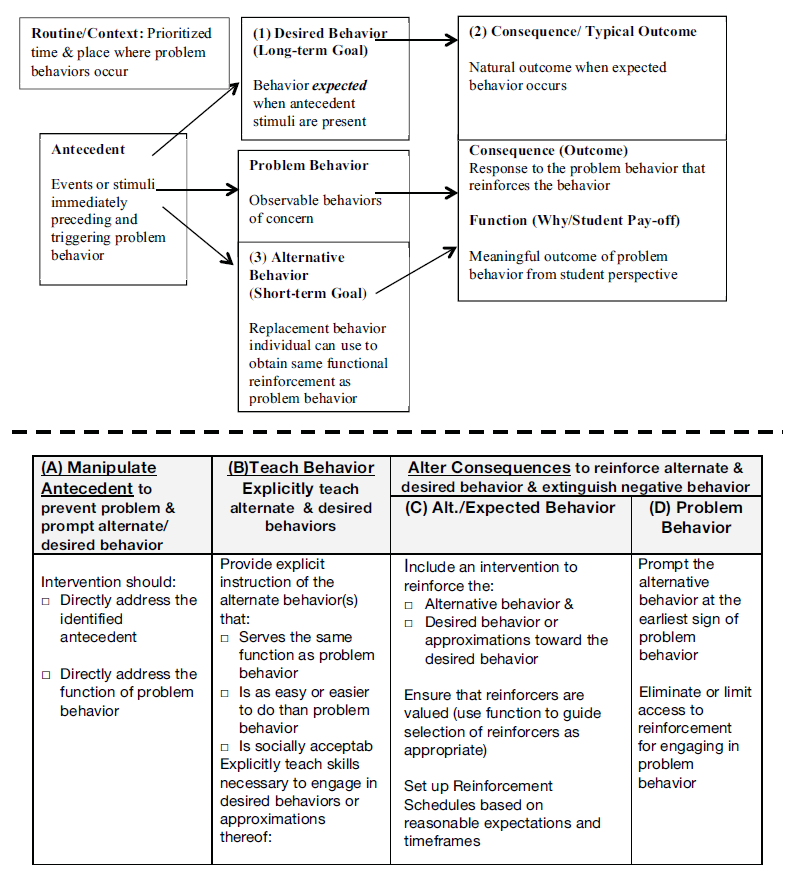
Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): Competing Behavior Pathway with Definitions of Critical Features
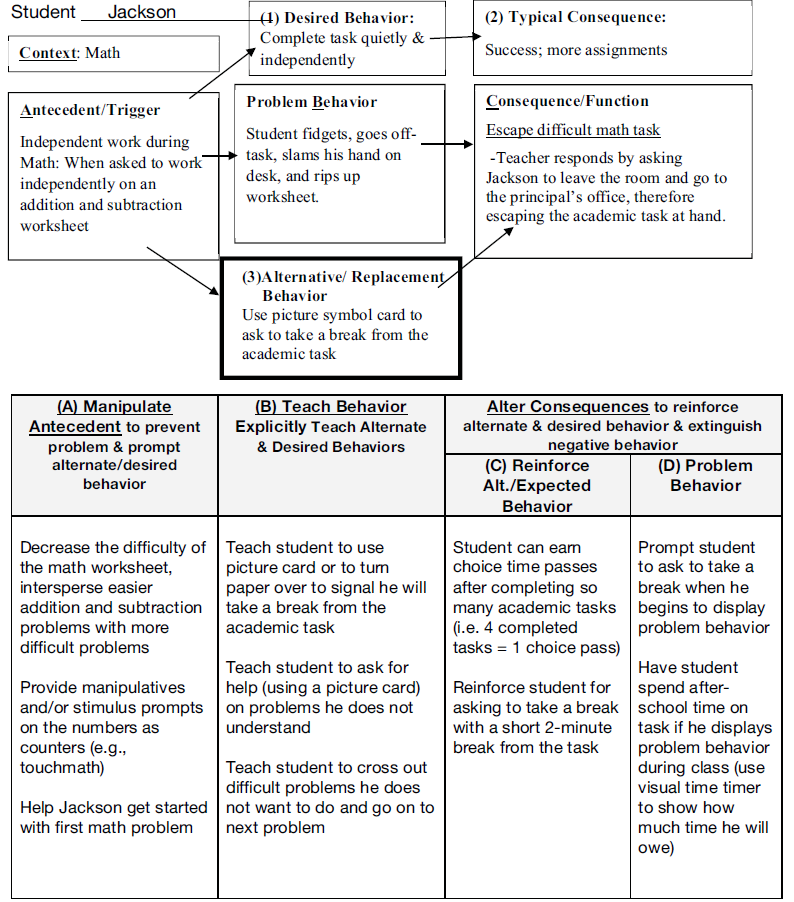
Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\): Example of Jackson’s Function-Based Support Plan
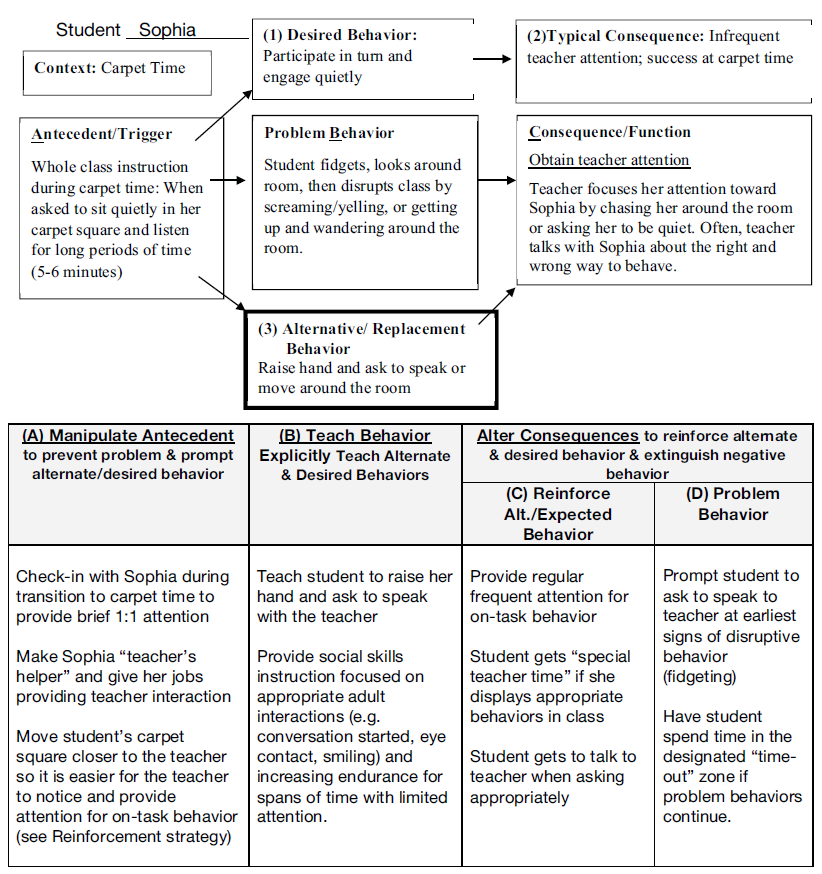
Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\): Example of Sophia’s Function-Based Support Plan

Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\): Essential Components for a Behavior Intervention Plan (from Loman, Strickland-
Cohen, & Borgmeier, 2013).
| Function of Behavior |
Antecedent Strategies Prevent problem behavior & support desired behavior Make problem behaviors irrelevant |
Behavior Teaching Strategies Teach replacement & desired behavior that gets results more quickly or easily to make the problem behavior inefficient. |
Consequence Strategies Change consequences that have supported rather than eliminated the problem behavior. Do NOT allow the negative behavior to pay off for the student, put the negative behavior on extinction Reward appropriate behavior to make the problem behavior ineffective. |
| Attention Seeking |
Prevention (give attention early for positive behaviors) Check-in – provide adult attention immediately upon student arrival Give student leadership responsibility or a class “job” that requires the student to interact w/ staff Place student in desk where they are easily accessible for frequent staff attention Give student frequent intermittent attention for positive or neutral behavior Pre-correct - Frequently & deliberately remind student to raise their hand and wait patiently if they want your attention |
Teach student more appropriate ways to ask for adult attention Identify and teach specific examples of ways to ask for attention
|
Respond quickly if student asks appropriately for adult attention Give the student frequent adult attention for positive behavior Student earns ‘lunch w/ teacher’ when student earns points for paying attention in class & asking appropriately for attention Eliminate/minimize the amount of attention provided to a student for engaging in problem behavior
|
| Function of Behavior | Antecedent Strategies | Behavior Teaching Strategies | Consequence Strategies |
| Avoid Task |
Prevention (modify task or provide support) Modify assignments to meet student instructional/skill level (adjust timelines, provide graphic organizers, break in to smaller chunks, etc.) Assign student to work with a peer Provide additional instruction/support Provide visual prompt to cue steps for completing tasks student struggles with Provide additional support focused on instructional skills (Homework Club, Study Hall, etc.) Pre-Teaching content Pre-Correct - Frequently & deliberately remind student to ask for help |
Teach student more appropriate ways to ask for help from teacher or peers Provide additional instruction on skill deficits Identify and teach specific examples of ways to ask for help Raise hand and wait patiently for teacher to call on you Teach student to use a break card
Provide academic instruction/support to address student skill deficits
|
Respond quickly if student asks for help or for a break Reward students for on task, trying hard, work completion & for asking for a break or help appropriately Eliminate/minimize the amount of missed instructional time or work provided to a student for engaging in problem behavior --However, need to make sure student is capable of doing work… or provide support/instruction so student can complete the work |


