7.7: Types of Natural Resources
- Page ID
- 62179
- Renewable resources: The renewable resources are freely available in nature and may be regenerated naturally. In this way these may be used for future. For examples forest (plants), animals, air, water, wind power, solar energy, geothermal energy, biomass etc.
- Non-renewable resources: The natural resources that are limited in numbers or cannot be renewed in short time are called non-renewable resources.
Causes of Exploitation:
-
Deforestation: Dam construction, mining and extension of agriculture land
-
Environmental Pollution: The air, water and land pollution are causes of natural resource degradation.
-
Development activities: Development activities like road construction and urbanization are responsible for Natural degradation.
Causes of Forest Exploitation:
Forest is an important resource for human development and it helps to balance the ecosystem. It is mandatory to have about 33% of forest cover area for a healthy ecosystem but due to several development activities we are losing forest cover.
There are several causes of deforestation you can understand it with the help of following points.
- Human population explosion: The population of the world is increasing day by day; to fulfil humans’ basic needs we are exploiting the forest land.
- Developmental activities: Development activities like mining, huge dams, or highways construction and railways lines, etc. are the responsible for the deforestation.
- Natural Disasters: Natural disasters like forest fires, landslides, snow avalanches, floods, droughts, volcanic eruptions, etc. are the responsible for the forest degradation.
- Over-grazing: Over-grazing is a common problem in developing countries. Every year due to over-grazing a large amount of forest areas become barren and soil becomes loose.
- Forest disease: Diseases in the forest are common problems that occur due to fungi, pests and insects. Every year thousands of hectares of forest land become destroyed due to the disease.
Sustainable Development
Our basic needs are provided by natural resources. Development is a continuous process in-human society. To utilize natural resources for the development of human society and simultaneously conserve these resources, a term was introduced which is called Sustainable Development. It can be understood with the help of Figure below.
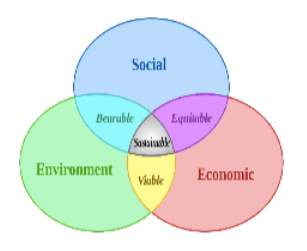
Sustainable development is commonly defined as “meeting the needs of the present generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.” In order to achieve a sustainable life, natural resources are necessary throughout the world, so that basic needs of each and every living being must be filled. The basic components which are required by every living being are fresh air, water, land (soil), plants and animals to survive in nature.
With the help of the following, one can conserve forest resources:
- The use of plantations to produce timber rather than logging in natural forests;
- Education and awareness regarding forest conservation;
- Strict laws and policies may help to conserve forests;
- Agro-forestry and social forestry plantations are helpful to conserve forests;
- Illegal trade in timber products must be prohibited;
- To create the reserve forest or protect the sites for wildlife conservation.
Ecotourism
Tourism is a large global economic activity. It helps to increase the revenue for nations but it was observed that this activity could pose a threat to natural resources, so a new concept of ecotourism was introduced by The International Ecotourism Society (TIES). According to TIES ecotourism is defined as “Responsible travel that promotes the conservation of nature and sustains the well-being of local people”.
Thus, ecotourism may be understood as
- Sustainable use of natural resources with benefits shared with the local citizens or stakeholders.
- The use of natural resources and indigenous knowledge that is shared to improve local socio economic standings.
- An environmental activity for the sustainable development of a human society and its culture.
Habitat Restoration
Habitat restoration holds considerable promise as a mechanism for restoring and maintaining biodiversity. Of course once a species has become extinct, its restoration is impossible. However, restoration can improve the biodiversity of degraded ecosystems. Reintroducing wolves, a top predator, to Yellowstone National Park in 1995 led to dramatic changes in the ecosystem that increased biodiversity. The wolves function to suppress elk and coyote populations and provide more abundant resources to the guild of carrion eaters. Reducing elk populations has allowed revegetation of riparian areas, which has increased the diversity of species in that habitat. Decreasing the coyote population has increased the populations of species that were previously suppressed by this predator. The number of species of carrion eaters has increased because of the predatory activities of the wolves. In this habitat, the wolf is a keystone species, meaning a species that is instrumental in maintaining diversity in an ecosystem.
Removing a keystone species from an ecological community may cause a collapse in diversity. The results from the Yellowstone experiment suggest that restoring a keystone species can have the effect of restoring biodiversity in the community. Ecologists have argued for the identification of keystone species where possible and for focusing protection efforts on those species; likewise, it also makes sense to attempt to return them to their ecosystem if they have been removed.

