5.2: Cognitive Development
- Page ID
- 70843
Early childhood is a time of pretending, blending fact and fiction, and learning to think of the world using language. As young children move away from needing to touch, feel, and hear about the world toward learning some basic principles about how the world works, they hold some pretty interesting initial ideas. For example, how many of you are afraid that you are going to go down the bathtub drain? Hopefully, none of you do! But a child of three might really worry about this as they sit at the front of the bathtub. A child might protest if told that something will happen “tomorrow” but be willing to accept an explanation that an event will occur “today after we sleep.” Or the young child may ask, “How long are we staying? From here to here?” while pointing to two points on a table. Concepts such as tomorrow, time, size and distance are not easy to grasp at this young age. Understanding size, time, distance, fact and fiction are all tasks that are part of cognitive development in the preschool years.
Preoperational Intelligence (Ob7, Ob8)
Piaget’s stage that coincides with early childhood is the preoperational stage. The word operational means logical, so these children were thought to be illogical. However, they were learning to use language or to think of the world symbolically. Let’s examine some Piaget’s assertions about children’s cognitive abilities at this age.
Pretend Play: Pretending is a favorite activity at this time. A toy has qualities beyond the way it was designed to function and can now be used to stand for a character or object unlike anything originally intended. A teddy bear, for example, can be a baby or the queen of a far away land!
Piaget believed that children’s pretend play helped children solidify new schemas they were developing cognitively. This play, then, reflected changes in their conceptions or thoughts. However, children also learn as they pretend and experiment. Their play does not simply represent what they have learned (Berk, 2007).
Egocentrism: Egocentrism in early childhood refers to the tendency of young children to think that everyone sees things in the same way as the child. Piaget’s classic experiment on egocentrism involved showing children a three dimensional model of a mountain and asking them to describe what a doll that is looking at the mountain from a different angle might see. Children tend to choose a picture that represents their own, rather than the doll’s view. However, when children are speaking to others, they tend to use different sentence structures and vocabulary when addressing a younger child or an older adult. This indicates some awareness of the views of others.
Syncretism: Syncretism refers to a tendency to think that if two events occur simultaneously, one caused the other. I remember my daughter asking that if she put on her bathing suit if it would turn to summer!
Animism: Animism refers to attributing life‐like qualities to objects. The cup is alive, the chair that falls down and hits the child’s ankle is mean, and the toys need to stay home because they are tired. Cartoons frequently show objects that appear alive and take on lifelike qualities. Young children do seem to think that objects that move may be alive but after age three, they seldom refer to objects as being alive (Berk, 2007).
Classification Errors: Preoperational children have difficulty understanding that an object can be classified in more than one way. For example, if shown three white buttons and four black buttons and asked whether there are more black buttons or buttons, the child is likely to respond that there are more black buttons. As the child’s vocabulary improves and more schemes are developed, the ability to classify objects improves.
Conservation of Liquid. Does pouring liquid in a tall, narrow container make it have more?
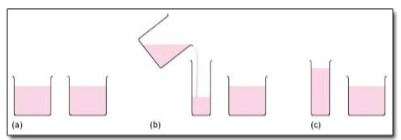
Conservation Errors: Conservation refers to the ability to recognize that moving or rearranging matter does not change the quantity. Imagine a two year old and a four year old eating lunch. The four year old has a whole peanut butter and jelly sandwich. He notices, however, that his younger sister’s sandwich is cut in half and protests, “She has more!”

