7.2: Ideological Spectrum
- Page ID
- 147648
Ideologies and the Ideological Spectrum
Ideologies can be placed on a spectrum for visual comparison. Liberal ideologies are traditionally put on the left and conservative ideologies on the right. (This placement dates from the French Revolution and is why liberals are called left-wing and conservatives are called right-wing.) The ideologies at the ends of the spectrum are the most extreme; those in the middle are moderate.
In the United States, ideologies at the right side of the spectrum prioritize government control over personal freedoms. They range from fascism to authoritarianism to conservatism. Ideologies on the left side of the spectrum prioritize equality and range from communism to socialism to liberalism. Moderate ideologies fall in the middle and try to balance the two extremes.

Definitions of Terms
Fascism promotes total control of the country by the ruling party or political leader. This form of government will run the economy, the military, society, and culture, and often tries to control the private lives of its citizens. Typically, there is an authoritarian leader.
Conservative governments attempt to hold tight to the traditions of a nation by balancing individual rights with the good of the community. Traditional conservatism supports the authority of the monarchy and the church, believing government provides the rule of law and maintains a society that is safe and organized. Modern conservatism differs from traditional conservatism in assuming elected government will guard individual liberties and provide laws. Modern conservatives also prefer a smaller government that stays out of the economy, allowing the market and business to determine prices, wages, and supply.
Classical liberalism believes in individual liberties and rights. It is based on the idea of free will, that people are born equal with the right to make decisions without government intervention. It views government with suspicion, since history includes many examples of monarchs and leaders who limited citizens’ rights. Today, modern liberalism focuses on equality and supports government intervention in society and the economy if it promotes equality. Liberals expect the government to provide basic social and educational programs to help everyone have a chance to succeed.
Under socialism, the government uses its authority to promote social and economic equality within the country. Socialists believe government should provide everyone with expanded services and public programs, such as health care, subsidized housing and groceries, childhood education, and inexpensive college tuition. Socialism sees the government as a way to ensure all citizens receive both equal opportunities and equal outcomes. Citizens with more wealth are expected to contribute more to the state’s revenue through higher taxes that pay for services provided to all. Socialist countries are also likely to have higher minimum wages than non-socialist countries.
In theory, communism promotes common ownership of all property, means of production, and materials. This means that the government, or states, should own the property, farms, manufacturing, and businesses. By controlling these aspects of the economy, Communist governments can prevent the exploitation of workers while creating an equal society. Extreme inequality of income, in which some citizens earn millions of dollars a year and other citizens merely hundreds, is prevented by instituting wage controls or by abandoning currency altogether. Communism presents a problem, however, because the practice differs from the theory. The theory assumes the move to communism is supported and led by the proletariat, or the workers and citizens of a country. Human rights violations by governments of actual Communist countries make it appear the movement has been driven not by the people, but by leadership.
Economic variations on these ideologies add another dimension to the ideological spectrum—whether we prefer that government control the state economy or stay out of it. The extremes are a command economy, such as existed in the former Soviet Russia, and a laissez-faire (“leave it alone”) economy, such as in the United States prior to the 1929 market crash, when banks and corporations were largely unregulated. Communism prioritizes control of both politics and economy, while libertarianism is its near-opposite. Libertarians believe government exists to maintain freedom and life, so its main function is to ensure domestic peace and national defense. Libertarians also believe the national government should maintain a military in case of international threats, but that it should not engage in setting minimum wages or ruling in private matters, like same-sex marriage or the right to abortion.
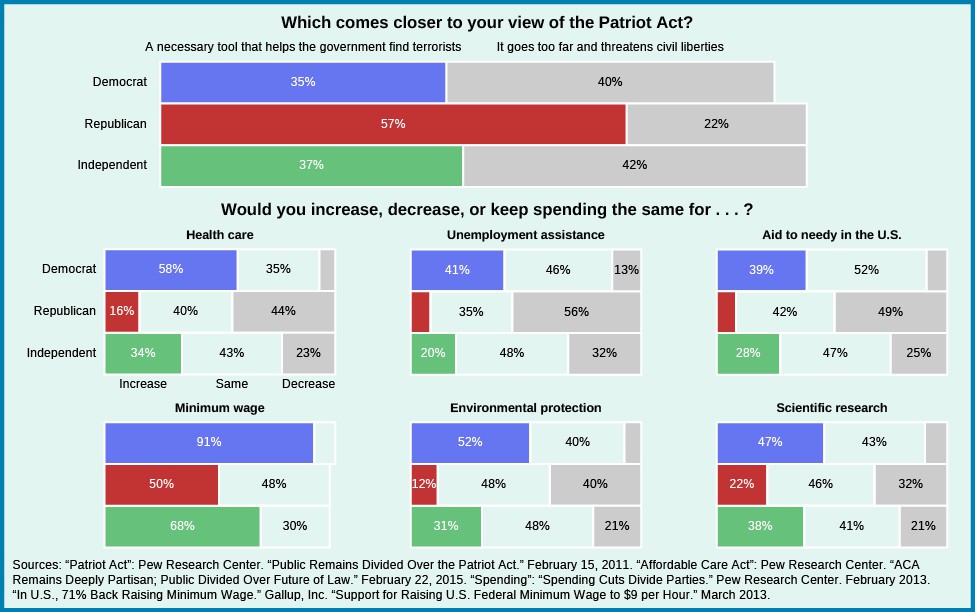
Though people can sometimes be liberal on one issue and conservative on another, a citizen to the left of liberalism, near socialism, would likely be happy with the passage of the Raise the Wage Act of 2015, which would eventually increase the minimum wage from $7.25 to $12 an hour. A citizen falling near conservatism would believe the Patriot Act is reasonable, because it allows the FBI and other government agencies to collect data on citizens’ phone calls and social media communications to monitor potential terrorism.
Summary of 7.1 and 7.2
Public opinion is more than a collection of answers to a question on a poll; it represents a snapshot of how people’s experiences and beliefs have led them to feel about a candidate, a law, or a social issue. Our attitudes are formed in childhood as part of our upbringing. They blend with our closely held beliefs about life and politics to form the basis for our opinions. Beginning early in life, we learn about politics from agents of socialization, which include family, schools, friends, religious organizations, and the media. Socialization gives us the information necessary to understand our political system and make decisions. We use this information to choose our ideology and decide what the proper role of government should be in our society.
- American Government 2e. Authored by: OpenStax. Located at: https://cnx.org/contents/nY32AU8S@5.1:xJJkKaSK@5/Preface. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/9d8df601-4f1...50bf739e5f@5.1

