8.3: Chapter 18- Psychosocial Development in Middle Childhood
- Page ID
- 55307
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Chapter 18 Learning Objectives
- Describe Erikson’s fourth stage of industry vs. inferiority
- Describe the changes in self-concept, self-esteem, and self-efficacy
- Explain Kohlberg’s stages of moral development
- Describe the importance of peers, the stages of friendships, peer acceptance, and the consequences of peer acceptance
- Describe bullying, cyberbullying and the consequences of bullying
- Identify the types of families where children reside
- Identify the five family tasks
- Explain the consequences of divorce on children
- Describe the effects of cohabitation and remarriage on children
- Describe the characteristics and developmental stages of blended families
Erikson: Industry vs. Inferiority
Self-Understanding

Kohlberg’s Stages of Moral Development
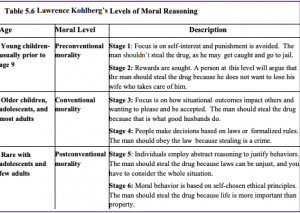
A man’s wife is dying of cancer and there is only one drug that can save her. The only place to get the drug is at the store of a pharmacist who is known to overcharge people for drugs. The man can only pay $1,000, but the pharmacist wants $2,000, and refuses to sell it to him for less, or to let him pay later. Desperate, the man later breaks into the pharmacy and steals the medicine. Should he have done that? Was it right or wrong? Why? (Kohlberg, 1984)
Level One-Preconventional Morality: In stage one, moral reasoning is based on concepts of punishment. The child believes that if the consequence for an action is punishment, then the action was wrong. In the second stage, the child bases his or her thinking on self-interest and reward. “You scratch my back, I’ll scratch yours.” The youngest subjects seemed to answer based on what would happen to the man as a result of the act. For example, they might say the man should not break into the pharmacy because the pharmacist might find him and beat him. Or they might say that the man should break in and steal the drug and his wife will give him a big kiss. Right or wrong, both decisions were based on what would physically happen to the man as a result of the act. This is a self-centered approach to moral decision-making. He called this most superficial understanding of right and wrong pre-conventional morality. Preconventional morality focuses on self-interest. Punishment is avoided, and rewards are sought. Adults can also fall into these stages, particularly when they are under pressure.
Level Two-Conventional Morality: Those tested who based their answers on what other people would think of the man as a result of his act, were placed in Level Two. For instance, they might say he should break into the store, and then everyone would think he was a good husband, or he should not because it is against the law. In either case, right and wrong is determined by what other people think. In stage three, the person wants to please others. At stage four, the person acknowledges the importance of social norms or laws and wants to be a good member of the group or society. A good decision is one that gains the approval of others or one that complies with the law. This he called conventional morality, people care about the effect of their actions on others. Some older children, adolescents, and adults use this reasoning.
Level Three-Postconventional Morality: Right and wrong are based on social contracts established for the good of everyone and that can transcend the self and social convention. For example, the man should break into the store because, even if it is against the law, the wife needs the drug and her life is more important than the consequences the man might face for breaking the law. Alternatively, the man should not violate the principle of the right of property because this rule is essential for social order. In either case, the person’s judgment goes beyond what happens to the self. It is based on a concern for others; for society as a whole, or for an ethical standard rather than a legal standard. This level is called post-conventional moral development because it goes beyond convention or what other people think to a higher, universal ethical principle of conduct that may or may not be reflected in the law. Notice that such thinking is the kind Supreme Court justices do all day when deliberating whether a law is moral or ethical, which requires being able to think abstractly. Often this is not accomplished until a person reaches adolescence or adulthood. In the fifth stage, laws are recognized as social contracts. The reasons for the laws, like justice, equality, and dignity, are used to evaluate decisions and interpret laws. In the sixth stage, individually determined universal ethical principles are weighed to make moral decisions. Kohlberg said that few people ever reach this stage. The six stages can be reviewed in Table 5.6.
Table 5.6
Friends and Peers

- Momentary physical interaction, a friend is someone who you are playing with at this point in time. Selman notes that this is typical of children between the ages of three and six. These early friendships are based more on circumstances (e.g., a neighbor) than on genuine similarities.
- One-way assistance, a friend is someone who does nice things for you, such as saving you a seat on the school bus or sharing a toy. However, children in this stage, do not always think about what they are contributing to the relationships. Nonetheless, having a friend is important and children will sometimes put up with a not so nice friend, just to have a friend. Children as young as five and as old as nine may be in this stage.
- Fair-weather cooperation, children are very concerned with fairness and reciprocity, and thus, a friend is someone returns a favor. In this stage, if a child does something Figure 5.21 Source Source 198 nice for a friend there is an expectation that the friend will do something nice for them at the first available opportunity. When this fails to happen, a child may break off the friendship. Selman found that some children as young as seven and as old as twelve are in this stage.
- Intimate and mutual sharing, typically between the ages of eight and fifteen, a friend is someone who you can tell them things you would tell no one else. Children and teens in this stage no longer “keep score” and do things for a friend because they genuinely care for the person. If a friendship dissolves in the stage it is usually due to a violation of trust. However, children in this stage do expect their friend to share similar interests and viewpoints and may take it as a betrayal if a friend likes someone that they do not.
- Autonomous interdependence, a friend is someone who accepts you and that you accept as they are. In this stage children, teens, and adults accept and even appreciate differences between themselves and their friends. They are also not as possessive, so they are less likely to feel threatened if their friends have other relationships or interests. Children are typically twelve or older in this stage.
Peer Relationships: Sociometric assessment measures attraction between members of a group, such as a classroom of students. In sociometric research children are asked to mention the three children they like to play with the most, and those they do not like to play with. The number of times a child is nominated for each of the two categories (like, do not like) is tabulated. Popular children receive many votes in the “like” category, and very few in the “do not like” category. In contrast, rejected children receive more unfavorable votes, and few favorable ones. Controversial children are mentioned frequently in each category, with several children liking them and several children placing them in the do not like category. Neglected children are rarely mentioned in either category, and the average child has a few positive votes with very few negative ones (Asher & Hymel, 1981).

Long-Term Consequences of Popularity: Childhood popularity researcher Mitch Prinstein has found that likability in childhood leads to positive outcomes throughout one’s life (as cited in Reid, 2017). Adults who were accepted in childhood have stronger marriages and work relationships, earn more money, and have better health outcomes than those who were unpopular. Further, those who were unpopular as children, experienced greater anxiety, depression, substance use, obesity, physical health problems and suicide. Prinstein found that a significant consequence of unpopularity was that children were denied opportunities to build their social skills and negotiate complex interactions, thus contributing to their continued unpopularity. Further, biological effects can occur due to unpopularity, as social rejection can activate genes that lead to an inflammatory response.
Bullying
Those at risk for bullying: Bullying can happen to anyone, but some students are at an increased risk for being bullied including lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgendered (LGBT) youth, those with disabilities, and those who are socially isolated. Additionally, those who are perceived as different, weak, less popular, overweight, or having low self-esteem, have a higher likelihood of being bullied. 200 Those who are more likely to bully: Bullies are often thought of as having low self-esteem, and then bully others to feel better about themselves. Although this can occur, many bullies in fact have high levels of self-esteem. They possess considerable popularity and social power and have well-connected peer relationships. They do not lack self-esteem, and instead lack empathy for others. They like to dominate or be in charge of others.
Those who are more likely to bully: Bullies are often thought of as having low self-esteem, and then bully others to feel better about themselves. Although this can occur, many bullies in fact have high levels of self-esteem. They possess considerable popularity and social power and have well-connected peer relationships. They do not lack self-esteem, and instead lack empathy for others. They like to dominate or be in charge of others.

Bullied children often do not ask for help: Unfortunately, most children do not let adults know that they are being bullied. Some fear retaliation from the bully, while others are too embarrassed to ask for help. Those who are socially isolated may not know who to ask for help or believe that no one would care or assist them if they did ask for assistance. Consequently, it is important for parents and teacher to know the warning signs that may indicate a child is being bullied. These include: unexplainable injuries, lost or destroyed possessions, changes in eating or sleeping patterns, declining school grades, not wanting to go to school, loss of friends, decreased selfesteem and/or self-destructive behaviors.
Family Life
Family Tasks: One of the ways to assess the quality of family life is to consider the tasks of families. Berger (2014) lists five family functions:
- Providing food, clothing and shelter
- Encouraging learning
- Developing self-esteem
- Nurturing friendships with peers
- Providing harmony and stability
Parenting Styles: As discussed in the previous chapter, parenting styles affect the relationship parents have with their children. During middle and late childhood, children spend less time with parents and more time with peers, and consequently parents may have to modify their approach to parenting to accommodate the child’s growing independence. The authoritative style, which incorporates reason and engaging in joint decision-making whenever possible may be the most effective approach (Berk, 2007). However, Asian-American, African-American, and Mexican-American parents are more likely than European-Americans to use an authoritarian style of parenting. This authoritarian style of parenting that uses strict discipline and focuses on obedience is also tempered with acceptance and warmth on the part of the parents. Children raised in this manner tend to be confident, successful and happy (Chao, 2001; Stewart & Bond, 2002).
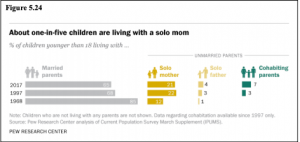
Living Arrangements: Certainly, the living arrangements of children have changed significantly over the years. In 1960, 92% of children resided with married parents, while only 5% had parents who were divorced or separated and 1% resided with parents who had never been married. By 2008, 70% of children resided with married parents, 15% had parent who were divorced or separated, and 14% resided with parents who had never married (Pew Research Center, 2010). In 2017, only 65% of children lived with two married parents, while 32% (24 million children younger than 18) lived with an unmarried parent (Livingston, 2018). Some 3% of children were not living with any parents, according to the U.S. Census Bureau data.
Figure 5.24
Lesbian and Gay Parenting: Research has consistently shown that the children of lesbian and gay parents are as successful as those of heterosexual parents, and consequently efforts are being made to ensure that gay and lesbian couples are provided with the same legal rights as heterosexual couples when adopting children (American Civil Liberties Union, 2016).

Divorce: Using families in the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD) Study of Early Child Care and Youth Development, Weaver and Schofield (2015) found that children from divorced families had significantly more behavior problems than those from a matched sample of children from non-divorced families. These problems were evident immediately after the separation and also in early and middle adolescence. An analysis of divorce factors indicated that children exhibited more externalizing behaviors if the family had fewer financial resources before the separation. It was hypothesized that the lower income and lack of educational and community resources contributed to the stress involved in the divorce. Additional factors contributing to children’s behavior problems included a post-divorce home that was less supportive and stimulating, and a mother that was less sensitive and more depressed.
Is cohabitation and remarriage more difficult than divorce for the child? The remarriage of a parent may be a more difficult adjustment for a child than the divorce of a parent (Seccombe & Warner, 2004). Parents and children typically have different ideas of how the stepparent should act. Parents and stepparents are more likely to see the stepparent’s role as that of parent. A more democratic style of parenting may become more authoritarian after a parent remarries. Biological parents are more likely to continue to be involved with their children jointly when neither parent has remarried. They are least likely to jointly be involved if the father has remarried and the mother has not. Cohabitation can be difficult for children to adjust to because cohabiting relationships in the United States tend to be short-lived. About 50 percent last less than 2 years (Brown, 2000). The child who starts a relationship with the parent’s live-in partner may have to sever this relationship later. Even in long-term cohabiting relationships, once it is over, continued contact with the child is rare.

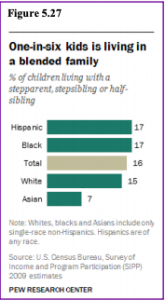
Blended Families: One in six children (16%) live in blended families (Pew Research Center, 2015). As can be seen in Figure 5.27, Hispanic, black and white children are equally likely to be living in a blended family. In contrast, children of Asian descent are more likely to be living with two married parents, often in their first marriage. Blended families are not new. In the 1700-1800s there were many blended families, but they were created because someone died and remarried. Most blended families today are a result of divorce and remarriage, and such origins lead to new considerations. Blended families are different from intact families and more complex in a number of ways that can pose unique challenges to those who seek to form successful blended family relationships (Visher & Visher, 1985). Children may be a part of two households, each with different rules that can be confusing.
Figure 5.27
References
Aiken, L. R. (1994). Psychological testing and assessment (8th ed.). Needham Heights, MA: Allyn and Bacon.
Alloway, T. P. (2009). Working memory, but not IQ, predicts subsequent learning in children with learning difficulties. European Journal of Psychological Assessment, 25, 92-98.
Alloway, T. P., Bibile, V., & Lau, G. (2013). Computerized working memory training: Can lead to gains in cognitive skills in students? Computers in Human Behavior, 29, 632-638.
American Civil Liberties Union (2016). Overview of lesbian and gay parenting, adoption and foster care. Retrieved from https://www.aclu.org/fact-sheet/over...nd-foster-care
American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association.
American Speech-Language and Hearing Association. (2016). Voice disorders. Retrieved from http://www.asha.org/PracticePortal/C...ice-Disorders/ Arditti, J. A. (1999). Rethinking relationships between divorced mothers and their children: Capitalizing on family strengths. Family Relations, 48, 109-119.
Anderson, J. (2018). The impact of family structure on the health of children: Effects of divorce. The Linacre Quarterly 81(4), 378–387.
Arkowicz, H., & Lilienfeld. (2013). Is divorce bad for children? Scientific American Mind, 24(1), 68-69. Figure 5.27 206
Asher, S. R., & Hymel, S. (1981). Children’s social competence in peer relations: Sociometric and behavioral assessment. In J. K. Wine & M. D. Smye (Eds.), Social competence (pp. 125-157). New York: Guilford Press.
Banaschewski, T., Becker, K., Döpfner, M., Holtmann, M., Rösler, M., & Romanos, M. (2017). Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. A current overview. Deutsches Ärzteblatt International, 114, 149-159.
Bandura, A. (1977). Self-efficacy: Toward a unifying theory of behavioral change. Psychological Review, 84, 191-215.
Bandura, A. (1986). Social foundations of thought and action: A social cognitive theory. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Bandura, A. (1997). Self-efficacy: The exercise of control. New York: Freeman.
Barnett, N. P., Smoll, F. L., & Smith, R. E. (1992). Effects of enhancing coach-athlete relationships on youth sport attrition. The Sport Psychologist, 6, 111-127.
Barbaresi, W. J., Colligan, R. C., Weaver, A. L., Voigt, R. G., Killian, J. M., & Katusic, S. K. (2013). Mortality, ADHD, and psychosocial adversity in adults with childhood ADHD: A prospective study. Pediatrics, 131, 637–644.
Barkley, R. A. (2006). Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: A handbook for diagnosis and treatment. New York, NY: Guilford Press.
Barkley, R. A., Fischer, M., Smallish, L., & Fletcher, K. (2002). The persistence of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder into young adulthood as a function of reporting source and definition of disorder. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 111, 279–289.
Beaulieu, C. (2004). Intercultural study of personal space: A case study. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 34(4), 794-805.
Berk, L. (2007). Development through the life span (4th ed.). Boston: Allyn and Bacon. Berger, K. S. (2014). The developing person: Through the life span. NY: Worth Publishers.
Bigelow, B. J. (1977). Children’s friendship expectations: A cognitive developmental study. Child Development, 48, 246–253.
Bigelow, B. J., & La Gaipa, J. J. (1975). Children’s written descriptions of friendship: A multidimensional analysis. Developmental Psychology, 11(6), 857-858.
Binet, A., Simon, T., & Town, C. H. (1915). A method of measuring the development of the intelligence of young children (3rd ed.) Chicago, IL: Chicago Medical Book.
Bink, M. L., & Marsh, R. L. (2000). Cognitive regularities in creative activity. Review of General Psychology, 4(1), 59–78.
Bjorklund, D. F. (2005). Children’s thinking: Developmental function and individual differences (4th ed.). Belmont, CA: Wadsworth.
Black, J. A., Park, M., Gregson, J. (2015). Child obesity cut-offs as derived from parental perceptions: Cross-sectional questionnaire. British Journal of General Practice, 65, e234-e239.
Boulton, M. J. (1999). Concurrent and longitudinal relations between children’s playground behavior and social preference, victimization, and bullying. Child Development, 70, 944-954.
Brody, N. (2003). Construct validation of the Sternberg Triarchic Abilities Test: Comment and reanalysis. Intelligence, 31(4), 319–329.
Bronfenbrenner, U. (1979). The ecology of human development: Experiments by nature and design. Cambridge, MA: Harvard Univeristy Press.
Brown, S. L. (2000). Union transitions among cohabitors: The significance of relationship assessments and expectations. Journal of Marriage and the Family, 62, 833-846. 207
Bruning, R. H., Schraw, G. J., Norby, M. M., & Ronning, R. R. (2004). Cognitive psychology and instruction. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson.
Burt, S. A. (2009). Rethinking environmental contributions to child and adolescent psychopathology: A meta-analysis of shared environmental influences. Psychological Bulletin, 135, 608–637.
Carlson, N. (2013). Physiology of behavior. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education.
Carlson, S. M., & Zelazo, P. D., & Faja, S. (2013). Executive function. In P. D. Zelazo (Ed.), The Oxford handbook of developmental psychology, Vol. 1: Body and mind (pp. 706-743). New York: Oxford University Press
Camarota, S. A., & Zeigler, K. (2015). One in five U. S. residents speaks foreign language at home. Retrieved from https://cis.org/sites/default/files/...anguage-15.pdf
Cazden, C. (2001). Classroom discourse, (2nd ed.). Portsmouth, NH: Heineman Publishers.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2000). 2000 CDC growth charts for the United States: Methods and development. Retrieved from http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/series/...1/sr11_246.pdf
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2010, November 12). Increasing prevalence of parent reported attentiondeficit/hyperactivity disorder among children, United States, 2003–2007. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, 59(44), 1439–1443.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2014). Birth defects. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/birthdefe...rome/data.html
Chao, R. (2001). Extending research on the consequences of parenting styles for Chinese Americans and European Americans. Child Development, 72, 1832-1843.
Cillesen, A. H., & Mayeaux, L. (2004). From censure to reinforcement: Developmental changes in the association between aggression and social status. Child Development, 75, 147-163.
Clark, M. L., & Bittle, M. L. (1992). Friendship expectations and the evaluation of present friendships in middle childhood and early adolescence. Child Study Journal, 22, 115–135.
Clay, R. A. (2013). Psychologists are using research-backed behavioral interventions that effectively treat children with ADHD. Monitor on Psychology, 44(2), 45-47.
Cohen, E. (2004). Teaching cooperative learning: The challenge for teacher education. Albany, NY: State University of New York Press.
Colangelo, N., & Assouline, S. (2009). Acceleration: Meeting the academic and social needs of students. In T. Balchin, B. Hymer, & D. J. Matthews (Eds.), The Routledge international companion to gifted education (pp. 194–202). New York, NY: Routledge.
Cowan, R., & Powell, D. (2014). The contributions of domain-general and numerical factors to third-grade arithmetic skills and mathematical learning disability. Journal of Educational Psychology, 106, 214-229.
Crain, W. (2005). Theories of development (5th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson.
Davidson, T. L. (2014). Do impaired memory and body weight regulation originate in childhood with diet-induced hippocampal dysfunction? The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 99(5), 971-972.
Davidson, T. L., Hargrave, S. L., Swithers, S. E., Sample, C. H., Fu, X., Kinzig, K. P., & Zheng, W. (2013). Inter-relationships among diet, obesity, and hippocampal-dependent cognitive function. Neuroscience, 253, 110-122.
de Ribaupierre, A. (2002). Working memory and attentional processes across the lifespan. In P. Graf & N. Ohta (Eds.), Lifespan of development of human memory (pp. 59-80). Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press. 208
Discover Esports. (2017). What are esports? Retrieved from https://discoveresports.com/what-are-esports/
Doolen, J., Alpert, P. T. and Miller, S. K. (2009), Parental disconnect between perceived and actual weight status of children: A metasynthesis of the current research. Journal of the American Academy of Nurse Practitioners, 21, 160–166. doi:10.1111/j.1745-7599.2008.00382.x
Drexler, P. (2005). Raising boys without men. Emmaus, PA: Rodale.
Dutton, E., van der Linden, D., Lynn, R. (2016). The negative Flynn effect: A systematic literature review. Intelligence, 59, 163- 169. Ennis, R. H. (1987). A taxonomy of critical thinking dispositions and abilities. In J. Baron & R. Sternberg (Eds.), Teaching thinking skills: Theory and practice (pp. 9-26). New York: Freeman.
Ericsson, K. (1998). The scientific study of expert levels of performance: General implications for optimal learning and creativity. High Ability Studies, 9(1), 75–100.
Erikson, E. (1982). The life cycle completed. NY: Norton & Company.
Flynn, J. R. (1999). Searching for justice: The discovery of IQ gains over time. American Psychologist, 54(1), 5–20.
Francis, N. (2006). The development of secondary discourse ability and metalinguistic awareness in second language learners. International Journal of Applied Linguistics, 16, 37-47.
Fraser-Thomas, J. L., Côté, J., & Deakin, J. (2005). Youth sport programs: An avenue to foster positive youth development. Physical Education & Sport Pedagogy, 10, 19-40.
Furnham, A., & Bachtiar, V. (2008). Personality and intelligence as predictors of creativity. Personality and Individual Differences, 45(7), 613–617.
Furstenberg, F. F., & Cherlin, A. J. (1991). Divided families: What happens to children when parents part. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Gardner, H. (1983). Frames of mind: The theory of multiple intelligences. New York: Basic Books.
Gardner, H. (1999). Intelligence reframed: Multiple intelligences for the 21st century. New York, NY: Basic Books.
Gilligan, C. (1982). In a different voice: Psychological theory and women’s development. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Gizer, I. R., Ficks, C., & Waldman, I. D. (2009). Candidate gene studies of ADHD: A meta-analytic review. Human Genetics, 126, 51–90.
Gottfredson, L. S. (1997). Mainstream science on intelligence: An editorial with 52 signatories, history and bibliography. Intelligence, 24(1), 13–23.
Gottfredson, L. S. (2003). Dissecting practical intelligence theory: Its claims and evidence. Intelligence, 31(4), 343–397.
Greenspan, S., Loughlin, G., & Black, R. S. (2001). Credulity and gullibility in people with developmental disorders: A framework for future research. In L. M. Glidden (Ed.), Internationalreview ofresearch in mental retardation (Vol. 24, pp. 101–135). San Diego, CA: Academic Press.
Guttmann, J. (1993). Divorce in psychosocial perspective: Theory and research. Hillsdale, NJ: L. Erlbaum Associates.
Haidt, J. (2001). The emotional dog and its rational tail: A social intuitionist approach to moral judgment. Psychological Review, 108(4), 814–834.
Hales, C.M., Carroll, M.D., Fryar, C.D., & Ogden, C.L. (2017). Prevalence of obesity among adults and youth: United States, 2015–2016. NCHS data brief, no 288. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics. 209
Halpern, D. F. (1992). Sex differences in cognitive abilities (2nd ed.). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Hansen, L., Umeda, Y., & McKinney, M. (2002). Savings in the relearning of second language vocabulary: The effects of time and proficiency. Language Learning, 52, 653-663.
Hartup, W. W. (1983). Adolescents and their friends. New Directions for Child and Adolescent Development, 60, 3-22.
Hennessey, B. A., & Amabile, T. M. (2010). Creativity. Annual Review of Psychology, 61, 569–598.
Hetherington, E. M., & Kelly, J. (2002). For better or for worse: Divorce reconsidered. New York: W.W. Norton.
Horvat, E. M. (2004). Moments of social inclusion and exclusion: Race, class, and cultural capital in family-school relationships. In A. Lareau (Author) & J. H. Ballantine & J. Z. Spade (Eds.), Schools and society: A sociological approach to education (2nd ed., pp. 276-286). Belmont, CA: Wadsworth.
Hoza, B., Mrug, S., Gerdes, A. C., Hinshaw, S. P., Bukowski, W. M., Gold, J. A., . . . Arnold, L. E. (2005). What aspects of peer relationships are impaired in children with ADHD? Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 73, 411–423.
Inhelder, B., & Piaget, J. (1958). The growth of logical thinking from childhood to adolescence. New York: Basic Books.
Jaffee, S., & Hyde, J. S. (2000). Gender differences in moral orientation: A meta-analysis. Psychological Bulletin, 126(5), 703– 726.
Jimenez, R., Garcia, G., & Pearson. D. (1995). Three children, two languages, and strategic reading: Case studies in bilingual/monolingual reading. American Educational Research Journal, 32 (1), 67-97. Johnson, D., & Johnson, R. (1998). Learning together and alone: Cooperative, competitive, and individualistic learning, (5th ed.). Boston: Allyn & Bacon.
Johnson, M. (2005). Developmental neuroscience, psychophysiology, and genetics. In M. Bornstein & M. Lamb (Eds.), Developmental science: An advanced textbook (5th ed., pp. 187-222).
Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum. Johnson, W., Carothers, A., & Deary, I. J. (2009). A role for the X chromosome in sex differences in variability in general intelligence? Perspectives on Psychological Science, 4(6), 598–611.
Kail, R. V., McBride-Chang, C., Ferrer, E., Cho, J.R., & Shu, H. (2013). Cultural differences in the development of processing speed. Developmental Science, 16, 476-483.
Katz, D. L. (2015). Oblivobesity: Looking over the overweight that parents keep overlooking. Childhood Obesity, 11(3), 225- 226.
Klein, R. G., Mannuzza, S., Olazagasti, M. A. R., Roizen, E., Hutchison, J. A., Lashua, E. C., & Castellanos, F. X. (2012). Clinical and functional outcome of childhood attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder 33 years later. Archives of General Psychiatry, 69, 1295–1303.
Klima, T., & Repetti, R. L. (2008). Children’s peer relations and their psychological adjustment: Differences between close friends and the larger peer group. Merrill-Palmer Quarterly, 54, 151-178.
Kohlberg, L. (1963). The development of children’s orientations toward a moral order: Sequence in the development of moral thought. Vita Humana, 16, 11-36.
Kohlberg, L. (1984). The psychology of moral development: Essays on moral development (Vol. 2, p. 200). San Francisco, CA: Harper & Row.
Kohnert, K., Yim, D., Nett, K., Kan, P., & Duran, L. (2005). Intervention with linguistically diverse preschool children. Language, Speech, and Hearing Services in Schools, 36, 251-263.
Lally, M. J., & Valentine-French, S. J. (2018). Introduction to Psychology [Adapted from Charles Stangor, Introduction to Psychology] Grayslake, IL: College of Lake County. 210
Liang, J., Matheson, B., Kaye, W., & Boutelle, K. (2014). Neurocognitive correlates of obesity and obesity-related behaviors in children and adolescents. International Journal of Obesity, 38(4), 494-506
Linnet, K. M., Dalsgaard, S., Obel, C., Wisborg, K., Henriksen, T. B., Rodriquez, A., . . . Jarvelin, M. R.(2003). Maternal lifestyle factors in pregnancy risk of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and associated behaviors: A review of current evidence. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 160, 1028–1040.
Livingston, G. (2018). About one-third of U.S. children are living with an unmarried parent. Retrieved from www.pewresearch.org/fact-tan...marriedparent/
Loe, I. M., & Feldman, H. M. (2007). Academic and educational outcomes of children with ADHD. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 32, 643–654.
Lofquist, D. (2011). Same-sex households. Current population reports, ACSBR/10-03. U.S. CensusBureau, Washington, DC. Retrieved from www.census.gov/prod/2011pubs/acsbr10-03.pdf
Lu, S. (2016). Obesity and the growing brain. Monitor on Psychology, 47(6), 40-43.
Lubinski, D., & Benbow, C. P. (2006). Study of mathematically precocious youth after 35 years: Uncovering antecedents for the development of math-science expertise. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 1(4), 316–345.
Macbeth, D. (2003). Hugh Mehan’s Learning Lessons reconsidered: On the differences between naturalistic and critical analysis of classroom discourse. American Educational Research Journal, 40 (1), 239-280.
Markant, J. C., & Thomas, K. M. (2013). Postnatal brain development. In P. D. Zelazo (Ed.), Oxford handbook of developmental psychology. New York: Oxford University Press.
Marshal, M. P., & Molina, B. S. G. (2006). Antisocial behaviors moderate the deviant peer pathway to substance use in children with ADHD. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 35, 216–226.
McCann, D., Barrett, A., Cooper, A., Crumpler, D., Dalen, L., Grimshaw, K., . . . Stevenson, J. (2007). Food additives and hyperactive behaviour in 3-year-old and 8/9-year-old children in the community: A randomised, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial. The Lancet, 370(9598), 1560–1567.
McGuine, T. A. (2016). The association of sports specialization and history of lower extremity injury in high school athletes. Medical Science in Sports and Exercise, 45 (supplement 5), 866.
McLanahan, S., & Sandefur, G. D. (1994). Growing up with a single parent: What hurts, what helps. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Medline Plus. (2016a). Phonological disorder. National Institute of Mental Health: U.S. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved from https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001541.htm
Medline Plus. (2016b). Speech and communication disorders. National Institute of Mental Health: U.S. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved from https://medlineplus.gov/speechandcom...disorders.html
Medline Plus. (2016c). Stuttering. National Institute of Mental Health: U.S. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved from https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/001427.htm
Miller, P. H. (2000). How best to utilize a deficiency? Child Development, 71, 1013-1017.
Minami, M. (2002). Culture-specific language styles: The development of oral narrative and literacy. Clevedon, UK: Multilingual Matters.
National Center for Learning Disabilities. (2017). The state of LD: Understanding the 1 in 5. Retrieved from https://www.ncld.org/archives/blog/t...ing-the-1-in-5
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. (2016). Dyslexia information page. Retrieved from https://www.ninds.nih.gov/Disorders/...formation-Page 211
National Institute on Deafness and other Communication Disorders. (2016). Stuttering. Retrieved from https://www.nidcd.nih.gov/health/stuttering
Neisser, U. (1997). Rising scores on intelligence tests. American Scientist, 85, 440-447.
Neisser, U. (1998). The rising curve. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Oude Luttikhuis, H., Stolk, R. and Sauer, P. (2010), How do parents of 4- to 5-year-old children perceive the weight of their children? Acta Pædiatrica, 99, 263–267. doi:10.1111/j.1651-2227.2009.01576.x
Patterson, C. J. (2013). Children of lesbian and gay parents: Psychology, law, and Policy. Psychology of Sexual Orientation and Gender Diversity, 1, 27-34.
Pettit, G. S., Clawson, M. A., Dodge, K. A., & Bates, J. E. (1996). Stability and change in peer-rejected status: The role of child behavior, parenting, and family ecology. Merrill-Palmer Quarterly, 42(2), 267-294.
Pew Research Center. (2010). New family types. Retrieved from www.pewsocialtrends.org/2010/...w-familytypes/
Pew Research Center. (2015). Parenting in America. Retrieved from www.pewresearch.org/wpconten...rica_FINAL.pdf
Plante, I., De la Sablonnière, R., Aronson, J. M., & Théorêt, M. (2013). Gender stereotype endorsement and achievement-related outcomes: The role of competence beliefs and task values. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 38(3), 225-235.
PreBler, A., Krajewski, K., & Hasselhorn, M. (2013). Working memory capacity in preschool children contributes to the acquisition of school relevant precursor skills. Learning and Individual Differences, 23, 138-144.
Public Law 93-112, 87 Stat. 394 (Sept. 26, 1973). Rehabilitation Act of 1973. Washington, D.C.: United States Government Printing Office.
Public Law 101-336, 104 Stat. 327 (July 26, 1990). Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990. Washington, D.C.: United States Government Printing Office.
Public Law 108-446, 118 Stat. 2647 (December 3, 2004). Individuals with Disabilities Education Improvement Act. Washington, D.C.: United States Government Printing Office.
Reid, S. (2017). 4 questions for Mitch Prinstein. Monitor on Psychology, 48(8), 31-32.
Rest, J. (1979). Development in judging moral issues. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press.
Retelsdorf, J., Asbrock, F., & Schwartz, K. (2015). “Michael can’t read!” teachers’ gender stereotypes and boys’ reading selfconcept. Journal of Educational Psychology, 107, 186-194.
Richter, D, & Lemola, S. (2017). Growing up with a single mother and life satisfaction in adulthood: A test of mediating and moderating factors. PLOS ONE 12(6): e0179639. Retrieved from https://journals.plos.org/plosone/ar...l.pone.0179639
Rogers, R., Malancharuvil-Berkes, E., Mosely, M., Hui, D., & O’Garro, G. (2005). Critical discourse analysis in education: A review of the literature. Review of Educational Research, 75 (3), 365-416.
Rogoff, B. (2003). The culture of human development. New York: Oxford University Press.
Rolls, E. (2000). Memory systems in the brain. Annual Review of Psychology, 51, 599-630.
Ross, H. S., & Lollis, S. P. (1989). A social relations analysis of toddler peer relations. Child Development, 60, 1082-1091.
Rubin, R. (1980). Children’s friendships. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Sabo, D., & Veliz, P. (2008). Go out and play: Youth sports in America. East Meadow, NY: Women’s Sports Foundation 212
Sarafrazi, N., Hughes, J. P., & Borrud, L. (2014). Perception of weight status in U.S. children and adolescents aged 8-15 years, 2005-2012. NCHS Data Brief, 158, 1-8.
Schneider, W., Kron-Sperl, V., & Hünnerkopf, M. (2009). The development of young children’s memory strategies: Evidence from the Würzburg Longitudinal Memory Study. European Journal of Developmental Psychology, 6, 70-99.
Schneider, W., & Pressley, M. (1997). Memory development between 2 and 20. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc.
Schwartz, D., Lansford, J. E., Dodge, K. A., Pettit, G. S., & Bates, J. E. (2014). Peer victimization during middle childhood as a lead indicator of internalizing problems and diagnostic outcomes in late adolescence. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 44, 393-404.
Seagoe, M. V. (1975). Terman and the gifted. Los Altos, CA: William Kaufmann.
Seccombe, K., & Warner, R. L. (2004). Marriages and families: Relationships in social context. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth/Thomson Learning.
Seifert, K. (2011). Educational psychology. Houston, TX: Rice University.
Selman, Robert L. (1980). The growth of interpersonal understanding. London: Academic Press.
Siegler, R. S. (1992). The other Alfred Binet. Developmental Psychology, 28(2), 179–190.
Simonton, D. K. (1992). The social context of career success and course for 2,026 scientists and inventors. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 18(4), 452–463.
Simonton, D. K. (2000). Creativity: Cognitive, personal, developmental, and social aspects. American Psychologist, 55(1), 151– 158.
Sodian, B., & Schneider, W. (1999). Memory strategy development: Gradual increase, sudden insight or roller coaster? In F. E. Weinert & W. Schneider (Eds.), Individual development from 3 to 12: Findings from the Munich Longitudinal Study (pp. 61-77). Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Sourander, A., Sucksdorff, M., Chudal, R, Surcel, H., Hinkka-Yli-Salomäki, S., Gyllenberg, D., Cheslack-Postava, K., & Brown, A. (2019). Prenatal cotinine levels and ADHD among offspring. Pediatrics, 143(3), e20183144.
Sport Policy and Research Collaborative (SPARC, 2013). What is the status of youth coach training in the U.S.? University of Florida. Retrieved from assets.aspeninstitute.org/co...0Brief%20Coach ing%20Education%20–%20FINAL.pdf
Sport Policy and Research Collaborative (SPARC, 2016). State of play 2016: Trends and developments. The Aspen Institute. Retrieved from https://www.aspeninstitute.org/publi...-developments/
Spreen, O., Rissser, A., & Edgell, D. (1995). Developmental neuropsychology. New York: Oxford University Press.
Sternberg, R. J. (1985). Beyond IQ: A triarchic theory of human intelligence. New York, NY: Cambridge University Press.
Sternberg, R. J. (2003). Contemporary theories of intelligence. In W. M. Reynolds & G. E. Miller (Eds.), Handbook of psychology: Educational psychology (Vol. 7, pp. 23–45). Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons.
Sternberg, R. J., Wagner, R. K., & Okagaki, L. (1993). Practical intelligence: The nature and role of tacit knowledge in work and at school. In J. M. Puckett & H. W. Reese (Eds.), Mechanisms of everyday cognition (pp. 205–227). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Stewart, A. J., Copeland, Chester, Malley, & Barenbaum. (1997). Separating together: How divorce transforms families. New York: Guilford Press.
Stewart, S. M. & Bond, M. H. (2002), A critical look at parenting research from the mainstream: Problems uncovered while adapting Western research to non-Western cultures. British Journal of Developmental Psychology, 20, 379–392. doi:10.1348/026151002320620389 213
Stopbullying.gov. (2018). Preventing weight-based bullying. Retrieved from https://www.stopbullying.gov/blog/20...-bullying.html
Swanson, J. M., Kinsbourne, M., Nigg, J., Lamphear, B., Stefanatos, G. A., Volkow, N., …& Wadhwa, P. D. (2007). Etiologic subtypes of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: brain imaging, molecular genetic and environmental factors and the dopamine hypothesis. Neuropsychological Review, 17(1), 39-59.
Tarasova, I. V., Volf, N. V., & Razoumnikova, O. M. (2010). Parameters of cortical interactions in subjects with high and low levels of verbal creativity. Human Physiology, 36(1), 80–85.
Terman, L. M., & Oden, M. H. (1959). Genetic studies of genius: The gifted group at mid-life (Vol. 5). Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
Thakur, G. A., Sengupta, S. M., Grizenko, N., Schmitz, N., Page, V., & Joober, R. (2013). Maternal smoking during pregnancy and ADHD: A comprehensive clinical and neurocognitive characterization. Nicotine and Tobacco Research, 15, 149– 157.
Tharp, R. & Gallimore, R. (1989). Rousing minds to life. New York: Cambridge University Press.
Thompson, A., Molina, B. S. G., Pelham, W., & Gnagy, E. M. (2007). Risky driving in adolescents and young adults with childhood ADHD. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 32, 745–759.
Torres-Guzman, M. (1998). Language culture, and literacy in Puerto Rican communities. In B. Perez (Ed.), Sociocultural contexts of language and literacy. Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
Treffert, D. A., & Wallace, G. L. (2004). Islands of genius. Scientific American, 14–23. Retrieved from http://gordonresearch.com/articles_a..._of_Genius.pdf
Tse, L. (2001). Why don’t they learn English? New York: Teachers’ College Press.
Turiel, E. (1998). The development of morality. In W. Damon (Ed.), Handbook of child psychology: Socialization (5th ed., Vol. 3, pp. 863–932). New York, NY: John Wiley & Sons.
United States Department of Education. (2017). Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA). Retrieved from https://www.ed.gov/essa?src=ft United States Youth Soccer. (2012).
US youth soccer at a glance. Retrieved from http://www.usyouthsoccer.org/media_kit/ataglance/
Vakil, E., Blachstein, H., Sheinman, M., & Greenstein, Y. (2009). Developmental changes in attention tests norms: Implications for the structure of attention. Child Neuropsychology, 15, 21-39.
van der Molen, M., & Molenaar, P. (1994). Cognitive psychophysiology: A window to cognitive development and brain maturation. In G. Dawson & K. Fischer (Eds.), Human behavior and the developing brain. New York: Guilford.
Visher, E. B., & Visher, J. S. (1985). Stepfamilies are different. Journal of Family Therapy, 7(1), 9-18.
Volkow N. D., Fowler J. S., Logan J., Alexoff D., Zhu W., Telang F., . . . Apelskog-Torres K. (2009). Effects of modafinil on dopamine and dopamine transporters in the male human brain: Clinical implications. Journal of the American Medical Association, 301, 1148–1154.
Wagner, R., & Sternberg, R. (1985). Practical intelligence in real-world pursuits: The role of tacit knowledge. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 49(2), 436–458.
Watkins, C. E., Campbell, V. L., Nieberding, R., & Hallmark, R. (1995). Contemporary practice of psychological assessment by clinical psychologists. Professional Psychology: Research and Practice, 26(1), 54–60.
Weaver, J. M., & Schofield, T. J. (2015). Mediation and moderation of divorce effects on children’s behavior problems. Journal of Family Psychology, 29(1), 39-48. doi:dx.doi.org/10.1037/fam0000043 214
Weir, K. (2019). Family-based behavioral treatment is key to addressing childhood obesity. Monitor on Pscyhology, 50(4), 31- 35.
Weisberg, R. (2006). Creativity: Understanding innovation in problem solving, science, invention, and the arts. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons.
Wilens, E., Fararone, S.V., Biederman, J., & Gunawardene, S. (2003). Does the treatment of Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder with stimulants contribute to use/abuse? Pediatrics, 111(1), 97-109.
Wolraich, M. L., Wilson, D. B., & White, J. W. (1995). The effect of sugar on behavior or cognition in children. Journal of the American Medical Association, 274, 1617–1621.
Attribution
Lifespan Development: A Psychological Perspective Second Edition by Martha Lally and Suzanne Valentine-French under the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 unported license.


