16.1: Persuasion- An Overview
- Page ID
- 79746
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Learning Objectives
- Define and explain persuasion.
- Explain the theory of persuasion discussed in the text: social judgment theory.
Persuasion: An Overview

NBS NewsHour – Podium – CC BY-NC 2.0.
In his text The Dynamics of Persuasion: Communication and Attitudes in the 21st Century, Richard Perloff noted that the study of persuasion today is extremely important for five basic reasons:
- The sheer number of persuasive communications has grown exponentially.
- Persuasive messages travel faster than ever before.
- Persuasion has become institutionalized.
- Persuasive communication has become more subtle and devious.
- Persuasive communication is more complex than ever before (Perloff, 2003).
In essence, the nature of persuasion has changed over the last fifty years as a result of the influx of various types of technology. People are bombarded by persuasive messages in today’s world, so thinking about how to create persuasive messages effectively is very important for modern public speakers. A century (or even half a century) ago, public speakers had to contend only with the words printed on paper for attracting and holding an audience’s attention. Today, public speakers must contend with laptops, netbooks, iPads, smartphones, billboards, television sets, and many other tools that can send a range of persuasive messages immediately to a target audience. Thankfully, scholars who study persuasion have kept up with the changing times and have found a number of persuasive strategies that help speakers be more persuasive.
What Is Persuasion?
We defined persuasion earlier in this text as an attempt to get a person to behave in a manner, or embrace a point of view related to values, attitudes, and beliefs, that he or she would not have done otherwise.
Change Attitudes, Values, and Beliefs
The first type of persuasive public speaking involves a change in someone’s attitudes, values, and beliefs. An attitude is defined as an individual’s general predisposition toward something as being good or bad, right or wrong, or negative or positive. Maybe you believe that local curfew laws for people under twenty-one are a bad idea, so you want to persuade others to adopt a negative attitude toward such laws.
You can also attempt to persuade an individual to change her or his value toward something. Value refers to an individual’s perception of the usefulness, importance, or worth of something. We can value a college education or technology or freedom. Values, as a general concept, are fairly ambiguous and tend to be very lofty ideas. Ultimately, what we value in life actually motivates us to engage in a range of behaviors. For example, if you value technology, you are more likely to seek out new technology or software on your own. On the contrary, if you do not value technology, you are less likely to seek out new technology or software unless someone, or some circumstance, requires you to.
Lastly, you can attempt to get people to change their personal beliefs. Beliefs are propositions or positions that an individual holds as true or false without positive knowledge or proof. Typically, beliefs are divided into two basic categories: core and dispositional. Core beliefs are beliefs that people have actively engaged in and created over the course of their lives (e.g., belief in a higher power, belief in extraterrestrial life forms). Dispositional beliefs, on the other hand, are beliefs that people have not actively engaged in but rather judgments that they make, based on their knowledge of related subjects, when they encounter a proposition. For example, imagine that you were asked the question, “Can stock cars reach speeds of one thousand miles per hour on a one-mile oval track?” Even though you may never have attended a stock car race or even seen one on television, you can make split-second judgments about your understanding of automobile speeds and say with a fair degree of certainty that you believe stock cars cannot travel at one thousand miles per hour on a one-mile track. We sometimes refer to dispositional beliefs as virtual beliefs (Frankish, 1998).
As we explained in Chapter 5 “Finding a Purpose and Selecting a Topic”, when it comes to persuading people to alter core and dispositional beliefs, persuading audiences to change core beliefs is more difficult than persuading audiences to change dispositional beliefs. For this reason, you are very unlikely to persuade people to change their deeply held core beliefs about a topic in a five- to ten-minute speech. However, if you give a persuasive speech on a topic related to an audience’s dispositional beliefs, you may have a better chance of success. While core beliefs may seem to be exciting and interesting, persuasive topics related to dispositional beliefs are generally better for novice speakers with limited time allotments.
Change Behavior
The second type of persuasive speech is one in which the speaker attempts to persuade an audience to change their behavior. Behaviors come in a wide range of forms, so finding one you think people should start, increase, or decrease shouldn’t be difficult at all. Speeches encouraging audiences to vote for a candidate, sign a petition opposing a tuition increase, or drink tap water instead of bottled water are all behavior-oriented persuasive speeches. In all these cases, the goal is to change the behavior of individual listeners.
Why Persuasion Matters
Frymier and Nadler enumerate three reasons why people should study persuasion (Frymier & Nadler, 2007). First, when you study and understand persuasion, you will be more successful at persuading others. If you want to be a persuasive public speaker, then you need to have a working understanding of how persuasion functions.
Second, when people understand persuasion, they will be better consumers of information. As previously mentioned, we live in a society where numerous message sources are constantly fighting for our attention. Unfortunately, most people just let messages wash over them like a wave, making little effort to understand or analyze them. As a result, they are more likely to fall for half-truths, illogical arguments, and lies. When you start to understand persuasion, you will have the skill set to actually pick apart the messages being sent to you and see why some of them are good and others are simply not.
Lastly, when we understand how persuasion functions, we’ll have a better grasp of what happens around us in the world. We’ll be able to analyze why certain speakers are effective persuaders and others are not. We’ll be able to understand why some public speakers can get an audience eating out of their hands, while others flop.
Furthermore, we believe it is an ethical imperative in the twenty-first century to be persuasively literate. We believe that persuasive messages that aim to manipulate, coerce, and intimidate people are unethical, as are messages that distort information. As ethical listeners, we have a responsibility to analyze messages that manipulate, coerce, and/or intimidate people or distort information. We also then have the responsibility to combat these messages with the truth, which will ultimately rely on our own skills and knowledge as effective persuaders.
Theories of Persuasion
Understanding how people are persuaded is very important to the discussion of public speaking. Thankfully, a number of researchers have created theories that help explain why people are persuaded. While there are numerous theories that help to explain persuasion, we are only going to examine one here: social judgment theory.
Social Judgment Theory
Muzafer Sherif and Carl Hovland created social judgment theory in an attempt to determine what types of communicative messages and under what conditions communicated messages will lead to a change in someone’s behavior (Sherif & Hovland, 1961). In essence, Sherif and Hovland found that people’s perceptions of attitudes, values, beliefs, and behaviors exist on a continuum including latitude of rejection, latitude of noncommitment, and latitude of acceptance (Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\) “Latitudes of Judgments”).
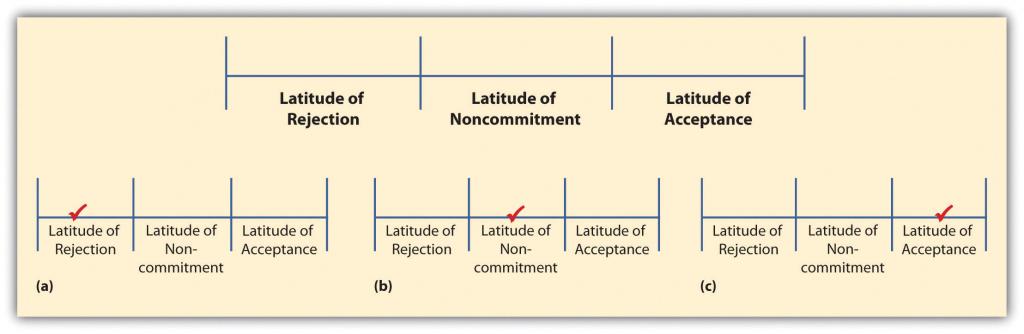
Imagine that you’re planning to persuade your peers to major in a foreign language in college. Some of the students in your class are going to disagree with you right off the bat (latitude of rejection, part (a) of Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\) “Latitudes of Judgments”). Other students are going to think majoring in a foreign language is a great idea (latitude of acceptance, part (c) of Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\) “Latitudes of Judgments”). Still others are really going to have no opinion either way (latitude of noncommitment, part (b) of Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\) “Latitudes of Judgments”). Now in each of these different latitudes there is a range of possibilities. For example, one of your listeners may be perfectly willing to accept the idea of minoring in a foreign language, but when asked to major or even double major in a foreign language, he or she may end up in the latitude of noncommitment or even rejection.
Not surprisingly, Sherif and Hovland found that persuasive messages were the most likely to succeed when they fell into an individual’s latitude of acceptance. For example, if you are giving your speech on majoring in a foreign language, people who are in favor of majoring in a foreign language are more likely to positively evaluate your message, assimilate your advice into their own ideas, and engage in desired behavior. On the other hand, people who reject your message are more likely to negatively evaluate your message, not assimilate your advice, and not engage in desired behavior.
In an ideal world, we’d always be persuading people who agree with our opinions, but that’s not reality. Instead, we often find ourselves in situations where we are trying to persuade others to attitudes, values, beliefs, and behaviors with which they may not agree. To help us persuade others, what we need to think about is the range of possible attitudes, values, beliefs, and behaviors that exist. For example, in our foreign language case, we may see the following possible opinions from our audience members:
- Complete agreement. Let’s all major in foreign languages.
- Strong agreement. I won’t major in a foreign language, but I will double major in a foreign language.
- Agreement in part. I won’t major in a foreign language, but I will minor in a foreign language.
- Neutral. While I think studying a foreign language can be worthwhile, I also think a college education can be complete without it. I really don’t feel strongly one way or the other.
- Disagreement in part. I will only take the foreign language classes required by my major.
- Strong disagreement. I don’t think I should have to take any foreign language classes.
- Complete disagreement. Majoring in a foreign language is a complete waste of a college education.
These seven possible opinions on the subject do not represent the full spectrum of choices, but give us various degrees of agreement with the general topic. So what does this have to do with persuasion? Well, we’re glad you asked. Sherif and Hovland theorized that persuasion was a matter of knowing how great the discrepancy or difference was between the speaker’s viewpoint and that of the audience. If the speaker’s point of view was similar to that of audience members, then persuasion was more likely. If the discrepancy between the idea proposed by the speaker and the audience’s viewpoint is too great, then the likelihood of persuasion decreases dramatically.

Furthermore, Sherif and Hovland predicted that there was a threshold for most people where attitude change wasn’t possible and people slipped from the latitude of acceptance into the latitude of noncommitment or rejection. Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\) “Discrepancy and Attitude Change” represents this process. All the area covered by the left side of the curve represents options a person would agree with, even if there is an initial discrepancy between the speaker and audience member at the start of the speech. However, there comes a point where the discrepancy between the speaker and audience member becomes too large, which move into the options that will be automatically rejected by the audience member. In essence, it becomes essential for you to know which options you can realistically persuade your audience to and which options will never happen. Maybe there is no way for you to persuade your audience to major or double major in a foreign language, but perhaps you can get them to minor in a foreign language. While you may not be achieving your complete end goal, it’s better than getting nowhere at all.
Key Takeaways
- Persuasion is the use of verbal and nonverbal messages to get a person to behave in a manner or embrace a point of view related to values, attitudes, and beliefs that he or she would not have done otherwise. Studying persuasion is important today because it helps us become more persuasive individuals, become more observant of others’ persuasive attempts, and have a more complete understanding of the world around us.
- Social judgment theory says that persuaders need to be aware of an audience’s latitudes of acceptance, noncommitment, and rejection in order to effectively persuade an audience.
Exercises
- Imagine you’re giving a speech to a group of college fraternity and sorority members about why hazing shouldn’t be tolerated. Explain the persuasive process using the theory of persuasion discussed in this chapter.
References
Festinger, L. (1957). A theory of cognitive dissonance. Evanston, IL: Row, Peterson, & Company.
Festinger, L., & Carlsmith, J. M. (1959). Cognitive consequences of forced compliance. Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 58, 203–210.
Frankish, K. (1998). Virtual belief. In P. Carruthers & J. Boucher (Eds.), Language and thought (pp. 249–269). Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Frymier, A. B., & Nadler, M. K. (2007). Persuasion: Integrating theory, research, and practice. Dubuque, IA: Kendall/Hunt.
Perloff, R. M. (2003). The dynamics of persuasion: Communication and attitudes in the 21st Century (2nd ed.). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum, pp. 5–6.
Petty, R. E., & Cacioppo, J. T. (1986). The elaboration likelihood model of persuasion. Advances in Experimental Social Psychology, 19, 123–205.
Sherif, M., & Hovland, C. I. (1961). Social judgment: Assimilation and contrast effects in communication and attitude change. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press.

